Are you concerned about finding the right lifting solution? Many people face challenges choosing between chains and wire ropes. This choice directly impacts safety and efficiency.
Wire ropes and chains serve similar purposes but have key differences. Wire ropes offer high strength-to-weight ratios and flexibility, making them ideal for many lifting and pulling applications, while chains are robust and resistant to abrasion.
I remember a time when a customer of mine, Andri, was working on a project. He needed to lift some heavy components. He was torn between using a chain or a wire rope, and he came to me for advice.
How Do Wire Ropes and Chains Differ in Construction?
Understanding their construction helps you see their strengths. Wire ropes are complex structures. It’s truly fascinating.
Wire ropes are made from multiple steel wires twisted into strands, which are then twisted around a core, while chains consist of interconnected metal links.

Unpacking Wire Rope Construction
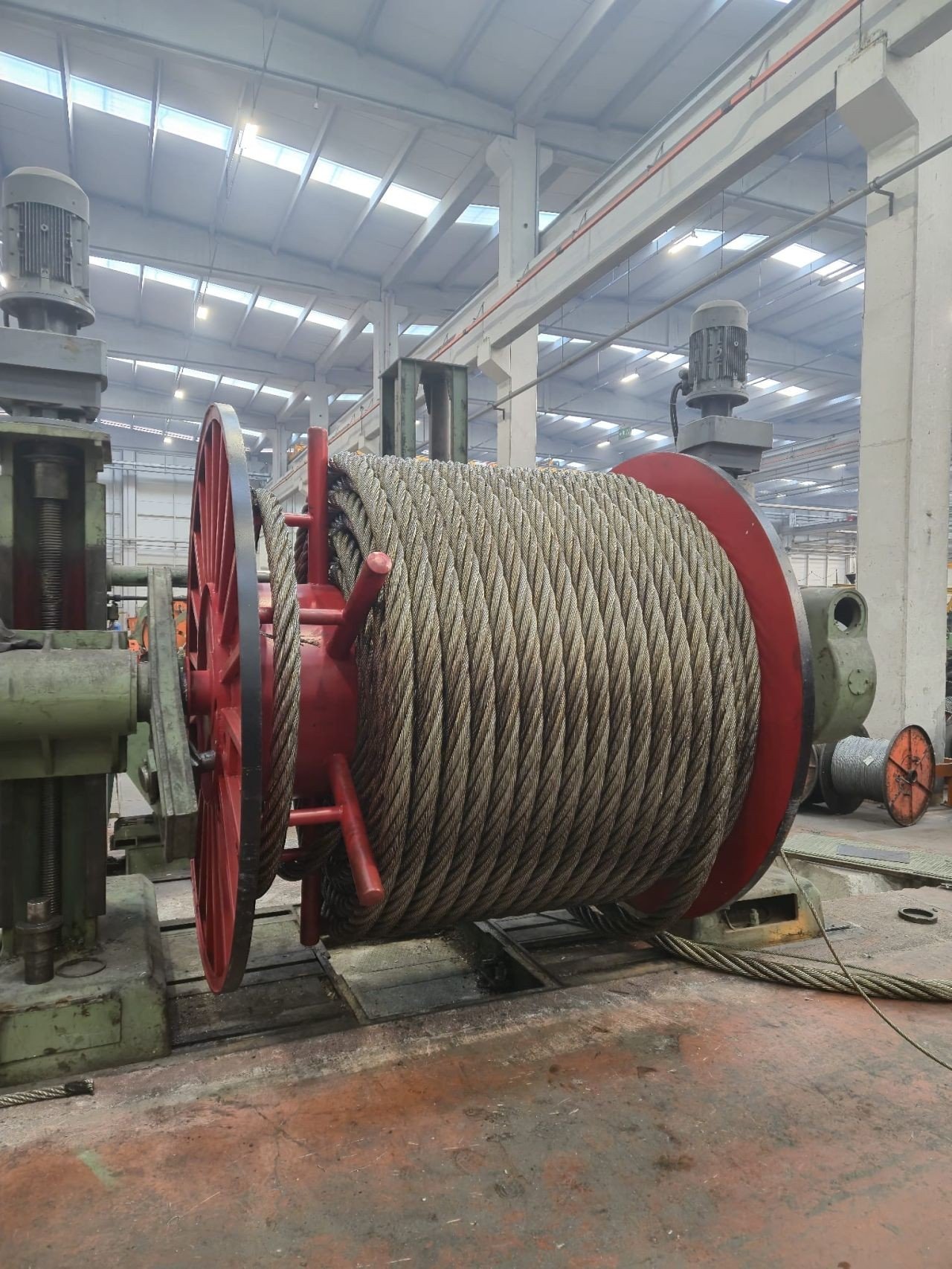
Wire ropes are engineered for specific tasks. My factory in China, Aulone, produces wire ropes with four production lines. We focus on high quality.
- Materials: We use high-carbon steel for our wire ropes. This gives them high tensile strength.
- What is high-carbon steel? It is steel with a carbon content between 0.6% and 1.0%. This makes it very hard.
- Why is this important? It allows the rope to handle heavy loads without breaking.
- Strands: Individual wires are twisted into strands.
- How are strands formed? Wires are spiraled together. This creates a strong, flexible unit.
- What does this do? It increases the rope’s strength and fatigue resistance.
- Core: Strands are laid around a core.
- What types of cores exist? Fiber cores (natural or synthetic) or steel cores (independent wire rope core – IWRC or wire strand core – WSC).
- Why have a core? It supports the strands and helps maintain the rope’s shape.
- Lay: The direction of the wire and strand twists.
- What are the common lays? Regular lay (wires and strands twisted in opposite directions) and Lang lay (wires and strands twisted in the same direction).
- How does lay affect performance? Regular lay offers good stability. Lang lay provides more flexibility and wear resistance.
Examining Chain Construction
Chains have a simpler, but equally effective, design.
- Materials: Chains are typically made from alloy steel.
- What kind of alloy steel? Grade 80 or Grade 100 alloy steel. These are heat-treated.
- Why use alloy steel? It provides high strength and durability. It resists corrosion.
- Links: Chains are formed by joining individual links.
- How are links connected? They are forged or welded together. This creates a continuous loop.
- What shapes do links have? Oval or round links are common. Some specialized links have unique shapes.
- Manufacturing Process: Links are formed and then heat-treated.
- What is heat treatment? It involves heating and cooling the metal. This changes its properties.
- Why is this done? It increases the chain’s hardness and strength. It also improves its fatigue life.
How Do Wire Ropes and Chains Perform Under Different Loads?
Performance under load is critical for safety. This is where the differences become very clear.
Wire ropes excel in tensile strength and dynamic loading, managing high breaking loads effectively, while chains are better suited for shock loading and environments where abrasion resistance is key.
Wire Rope Load Performance
Wire ropes are designed for heavy lifting. Our products, for example, comply with EN12385-4. This means they meet strict safety standards.
- Tensile Strength: This is the maximum stress a material can withstand.
- How high is it for wire ropes? Very high. We ensure our ropes have high tensile strength.
- Why is this important? It dictates how much weight the rope can lift safely.
- Breaking Load: The actual load at which a wire rope breaks.
- How do we achieve a high breaking load? Through careful material selection and manufacturing processes.
- What does a high breaking load mean? It means a larger margin of safety during operations.
- Dynamic Loading: Moving or changing loads.
- How do wire ropes handle dynamic loads? Their flexibility and elasticity help absorb shocks.
- Where is this useful? In cranes and elevators, where loads move frequently.
- Fatigue Resistance: The ability to withstand repeated stress cycles.
- Are wire ropes good for this? Yes, if properly maintained.
- Why does this matter? It extends the service life of the rope. It prevents unexpected failures.
Chain Load Performance
Chains are known for their ruggedness.
- Shock Loading: Sudden, forceful impacts.
- How do chains react? They can absorb significant shock loads. Their links allow some stretch.
- Where is this beneficial? In situations where loads might be dropped or suddenly applied.
- Abrasion Resistance: The ability to withstand surface wear.
- Are chains resistant to abrasion? Yes, more so than wire ropes.
- Why is this an advantage? In abrasive environments like mining, chains last longer.
- Load Distribution: How weight is spread across the structure.
- How do chains distribute load? Each link takes a portion of the load. This can cause deformation in individual links if overloaded.
- What are the implications? It’s important to monitor chain wear closely.
When Should You Use Wire Ropes Versus Chains?
The application dictates the best choice. I always advise my customers to consider their specific needs.
Wire ropes are generally preferred for applications requiring high lifting heights, speed, and flexibility, such as cranes and elevators, while chains are often chosen for short lifts, harsh environments, and situations needing high durability.
Ideal Applications for Wire Ropes
Our wire ropes are used globally. We serve Singapore, Indonesia, and Australia, among others.
- Cranes: From massive construction cranes to smaller workshop models.
- Why wire ropes? They offer the necessary length, flexibility, and strength. They allow smooth, controlled lifting.
- My experience: Many of our crane wire ropes are plastic impregnated. This improves durability.
- Elevators: Passenger and freight elevators.
- Why wire ropes? Smooth operation and high safety factors are crucial.
- Further considerations: Elevator ropes often have specific constructions. They balance flexibility and non-rotating properties.
- Mining: Shovels, draglines, and hoists.
- Why wire ropes? They handle heavy, continuous loads. They resist wear from abrasive materials.
- What features are important? High breaking load and good fatigue resistance.
- Marine and Offshore: Mooring lines, towing, and lifting on vessels.
- Why wire ropes? They offer high strength and can be galvanized for corrosion resistance.
- What about synthetic ropes? We also offer synthetic ropes for marine applications, which are lighter and float.
- Specialized Assemblies: Custom-made solutions.
- What are these? Wire ropes fitted with specific end terminals.
- When are they used? When standard ropes don’t fit the requirement. We make these for customers.
Best Uses for Chains
Chains excel in specific demanding conditions.
- Slinging and Rigging (Short Lifts): Moving irregular loads over short distances.
- Why chains? Their ability to conform to unusual shapes. Their resistance to cutting edges.
- Consideration: Check for kinks and bends regularly.
- Securement: Tying down heavy equipment or loads.
- Why chains? Their robust nature and resistance to stretching.
- Important: Ensure proper tensioning and use appropriate binders.
- Harsh Environments: Where extreme temperatures or corrosive materials are present.
- Why chains? They are less susceptible to damage from sharp edges or heat.
- Example: Foundry work or logging.
- Recovery and Towing (Heavy Duty): For pulling large vehicles or machinery.
- Why chains? Their sheer strength and ability to withstand sudden jerks.
- Note: Always use chains rated for the specific weight.
What Maintenance and Inspection Practices are Needed?
Proper maintenance ensures longevity and safety. This is something I discuss with all my clients.
Both wire ropes and chains require regular inspection and maintenance, but the specific practices differ, with wire ropes needing careful lubrication and visual checks for broken wires, while chains need cleaning and checks for stretched or damaged links.
Maintaining Wire Ropes
My team always emphasizes pro-active maintenance to our clients.
- Lubrication: Applying oil or grease to the rope.
- Why lubricate? It reduces friction between wires. It prevents corrosion.
- How often? Depends on usage and environment. Often, it’s done periodically.
- Visual Inspection: Looking for signs of wear.
- What to look for? Broken wires, corrosion, deformation, kinks, or crushing.
- When to inspect? Before each use, and more thoroughly at regular intervals.
- Measuring Diameter: Checking for reduction in size.
- Why measure? A significant reduction indicates internal wear or core damage.
- Tool: Use calipers.
- End Fittings: Inspecting the connection points.
- What to check? For cracks, wear, or improper attachment.
- Importance: End fittings are critical for load transfer.
Maintaining Chains
Chains, while robust, are not maintenance-free.
- Cleaning: Removing dirt and debris.
- Why clean? To make inspection easier. To prevent abrasive particles from causing wear.
- Method: Use wire brushes or appropriate cleaning solutions.
- Link Inspection: Checking individual links.
- What to look for? Stretched links, nicks, gouges, cracks, or signs of heat damage.
- Tool: Go/no-go gauge for link elongation.
- Measurement: Checking for elongation over a certain number of links.
- Why measure? Elongation indicates wear and potential failure.
- Standard: Check against manufacturer’s specifications.
- Proof Testing: Applying a load to ensure integrity.
- When is this done? After repairs or significant use, usually in specialized facilities.
- Purpose: To verify the chain’s capacity.
What are the Safety and Certification Requirements?
Safety is my top priority. My factory prides itself on providing products with certifications like BV, CE, RMRS, DNV, and ABS.
Safety standards for wire ropes and chains are governed by international and national bodies, requiring compliance with specifications like EN12385-4 for wire ropes, and Mandating regular inspections, proof testing, and certifications for both to ensure safe operation and traceability.
Wire Rope Safety and Certification
Certifications provide assurance of quality and safety.
- EN12385-4: A European standard for steel wire ropes for general lifting applications.
- What does it cover? Requirements for materials, manufacture, testing, and inspection.
- Why is it important? It provides a benchmark for quality and performance.
- Breaking Strength Calculation: Determining the ultimate load capacity.
- How is it done? Theoretical calculations based on wire and strand properties, and empirical testing.
- Safety Factor: Always apply a safety factor to the breaking strength. This ensures safe working load.
- Certifications: Official documents confirming compliance.
- Which ones do we offer? BV & CE, RMRS, DNV, ABS.
- Why are these important? They show that the product has met rigorous standards. They are often required for international trade.
- Traceability: The ability to track a product’s history.
- Why is it important? For quality control, recall procedures, and accountability.
- How do we ensure it? Through meticulous record-keeping and unique product identifiers.
Chain Safety and Certification
Chains also have strict safety guidelines.
- ASME B30.9: American Society of Mechanical Engineers standard for slings.
- What does it cover? Design, inspection, testing, and use of slings, including chain slings.
- Importance: Provides guidelines for safe use in the United States.
- OSHA Requirements: Occupational Safety and Health Administration guidelines.
- What do they state? Federal regulations for workplace safety, including lifting equipment.
- Compliance: Employers must adhere to these rules.
- Load Indicators: Devices that show the force being applied to the chain.
- How do they work? They measure tension or sag.
- Benefit: Helps prevent overloading.
- Link Grade Marking: Stamping on links indicating the material grade.
- Why is it important? It allows users to quickly identify the chain’s strength capacity.
- Example: G80 for Grade 80 alloy steel.
Conclusion
Choosing between wire ropes and chains depends on the task. Wire ropes offer high strength and flexibility, while chains provide durability and abrasion resistance. Both require careful selection and maintenance.