Shackles Manufacturer
Overview of Shackles
Shackles are pivotal components in the rigging and lifting industry, used to connect lifting equipment to loads. They are designed for quick and secure attachment and detachment, making them indispensable in many operations across various industries.
Types of Shackles
D-Shackle (Chain Shackle):
- Shape: D-shaped, more robust and narrower than a bow shackle.
- Use: Best suited for straight-line applications, such as lifting, where the load directly aligns with the shackle.
Bow Shackle (Anchor Shackle):
- Shape: Bow-shaped or an oval loop, providing a larger area.
- Use: Ideal for multi-dimensional loading, tolerating off-axis stress better than D-shackles. Suitable when load movement might cause shackle rotation.
Pin Types
- Screw Pin Shackles: Feature a threaded pin that is hand-tightened into the shackle, ideal for quick, temporary applications.
- Safety Pin Shackles: Equipped with a pin secured by a nut and a split pin (cotter pin), ideal for permanent or semi-permanent applications where the load remains constant.
Materials and Construction
- Carbon Steel: Commonly used for general lifting purposes due to its toughness and durability.
- Alloy Steel: Offers higher strength and fatigue resistance, preferred for heavy-duty and critical applications.
- Stainless Steel: Used in environments where corrosion resistance is crucial, such as marine applications.
Safety and Compliance
- Load Ratings: Each shackle is marked with a Working Load Limit (WLL), which must never be exceeded.
- Standards and Certifications: Shackles should meet specific standards such as ASTM or ISO to ensure reliability and safety.
- Inspection and Maintenance: Regular checks for wear, deformation, and damage are essential, with more frequent inspections required under harsh conditions.
Applications
- Construction: Used in cranes, hoists, and other lifting devices to attach loads securely.
- Marine: Essential for mooring, anchoring, and towing operations, where resistance to corrosion and strength are vital.
- Industrial: Utilized in manufacturing facilities for assembly lines, machinery moving, and heavy load management.
- Entertainment Industry: Employed in staging and rigging for events to safely hang lighting, sound equipment, and set pieces.
Selection Tips
- Choosing the Right Type: Opt for a bow shackle for shifting or multidirectional forces, and a D-shackle for direct, static loads.
- Size and Pin Selection: Ensure the shackle size and pin type are appropriate for the application’s security needs.
- Environment Consideration: Select materials and coatings based on environmental exposure, such as stainless steel for marine applications to prevent rust.
Understanding the correct application and maintenance of shackles is crucial to ensuring the safety and efficiency of lifting operations in various industries.
US Type Bow Shackle G209/ G213
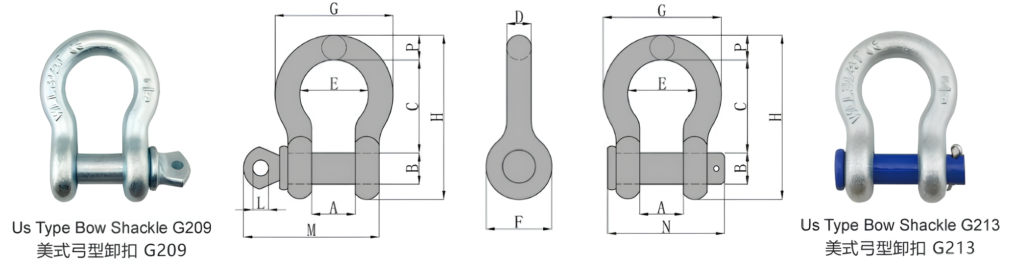
Feature:
- Material: Body 45# Carbon Steel, Pin 40Cr Alloy Steel
- Technology: Drop Forged
- Surface Finish: Electro Galvanized, Hot Dip Galvanized, Dacromet, Powder Coated
- Ultimate Load: 4 times or 6 times of the WILL
- Heat Treatment: 6 times
- WLL: 1/2-55T
- Usage: Lifting and connecting, Wire rope fittings, chain fittings, Maring hardware fittings
Parameters
| Size (in) | WLL (t) | Dimensions(in) | Weight (lbs) | |||||||||||
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | L | M | N | P | |||
| 1/4 | 1/2 | 0.47 | 0.31 | 1.13 | 0.25 | 0.78 | 0.61 | 1.28 | 1.84 | 0.19 | 1.38 | 1.34 | 0.25 | 0.12 |
| 5/16 | 3/4 | 0.53 | 0.38 | 1.22 | 0.31 | 0.84 | 0.75 | 1.47 | 2.09 | 0.22 | 1.66 | 1.59 | 0.31 | 0.19 |
| 3/8 | 1 | 0.66 | 0.44 | 1.44 | 0.38 | 1.03 | 0.91 | 1.78 | 2.49 | 0.25 | 2.03 | 1.86 | 0.38 | 0.31 |
| 7/16 | 1 1/2 | 0.75 | 0.50 | 1.69 | 0.44 | 1.16 | 1.06 | 2.03 | 2.91 | 0.31 | 2.38 | 2.13 | 0.44 | 0.38 |
| 1/2 | 2 | 0.81 | 0.63 | 1.88 | 0.5 | 1.31 | 1.19 | 2.31 | 3.28 | 0.38 | 2.69 | 2.38 | 0.5 | 0.63 |
| 5/8 | 3 1/4 | 1.06 | 0.75 | 2.38 | 0.63 | 1.69 | 1.50 | 2.94 | 4.19 | 0.44 | 3.34 | 2.91 | 0.69 | 1.38 |
| 3/4 | 4 3/4 | 1.25 | 0.88 | 2.81 | 0.75 | 2.00 | 1.81 | 3.50 | 4.97 | 0.50 | 3.97 | 3.44 | 0.81 | 2.25 |
| 7/8 | 6 1/2 | 1.44 | 1.00 | 3.31 | 0.88 | 2.28 | 2.09 | 4.03 | 5.83 | 0.50 | 4.50 | 3.81 | 0.97 | 3.38 |
| 1 | 8 1/2 | 1.69 | 1.13 | 3.75 | 1.00 | 2.69 | 2.38 | 4.69 | 6.56 | 0.56 | 5.07 | 4.53 | 1.06 | 5.32 |
| 1 1/8 | 9 1/2 | 1.81 | 1.25 | 4.25 | 1.16 | 2.91 | 2.69 | 5.16 | 7.47 | 0.63 | 5.59 | 5.13 | 1.25 | 6.81 |
| 1 1/4 | 12 | 2.03 | 1.38 | 4.69 | 1.29 | 3.25 | 3.00 | 5.75 | 8.25 | 0.69 | 6.16 | 5.5 | 1.38 | 9.50 |
| 1 3/8 | 13 1/2 | 2.25 | 1.50 | 5.25 | 1.42 | 3.63 | 3.31 | 6.38 | 9.16 | 0.75 | 6.84 | 6.13 | 1.50 | 13.25 |
| 2 1/2 | 17 | 2.38 | 1.63 | 5.75 | 1.54 | 3.88 | 3.63 | 6.88 | 10.00 | 0.81 | 7.35 | 6.5 | 1.62 | 17.20 |
| 1 3/4 | 25 | 2.88 | 2.00 | 7.00 | 1.84 | 5.00 | 4.19 | 8.86 | 12.34 | 1.00 | 9.08 | 7.75 | 2.25 | 30.38 |
| 2 | 35 | 3.25 | 2.25 | 7.75 | 2.08 | 5.75 | 4.81 | 9.97 | 13.68 | 1.22 | 10.34 | 8.75 | 2.40 | 45.00 |
| 2 1/2 | 55 | 4.13 | 2.75 | 10.5 | 2.71 | 7.25 | 5.69 | 12.87 | 17.84 | 1.38 | 13.00 | – | 3.13 | 85.75 |
US Type Dee Shackle G210/G215
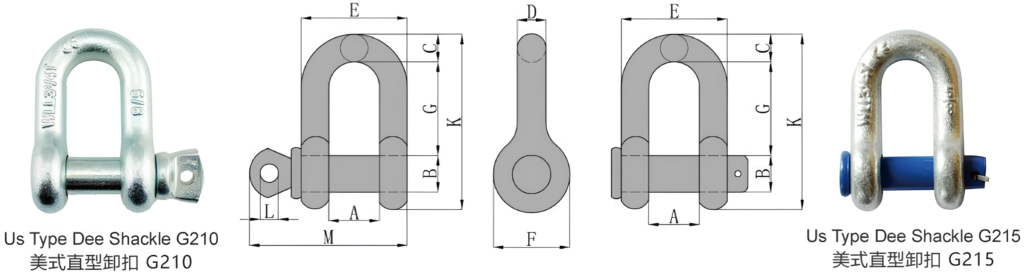
Feature:
- Material: Body 45# Carbon Steel, Pin 40Cr Alloy Steel
- Technology: Drop Forged
- Surface Finish: Electro Galvanized, Hot Dip Galvanized, Dacromet, Powder Coated
- Ultimate Load: 4 times or 6 times of the WILL
- Heat Treatment: 6 times
- WLL: 1/2-55T
- Usage: Lifting and connecting, Wire rope fittings, chain fittings, Maring hardware fittings
Parameters
| Size (in) | WLL (t) | Dimensions(in) | Weight (lbs) | |||||||||
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | K | L | M | |||
| 1/4 | 1/2 | 0.47 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.97 | 0.62 | 0.97 | 1.59 | 0.19 | 1.43 | 0.11 |
| 5/16 | 3/4 | 0.53 | 0.38 | 0.31 | 0.31 | 1.15 | 0.75 | 1.07 | 1.91 | 0.22 | 1.71 | 0.17 |
| 3/8 | 1 | 0.66 | 0.44 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 1.42 | 0.92 | 1.28 | 2.31 | 0.25 | 2.02 | 0.24 |
| 7/16 | 1 1/2 | 0.75 | 0.50 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 1.63 | 1.06 | 1.48 | 2.67 | 0.31 | 2.37 | 0.40 |
| 1/2 | 2 | 0.81 | 0.63 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 1.81 | 1.18 | 1.66 | 3.03 | 0.38 | 2.69 | 0.59 |
| 5/8 | 3 1/4 | 1.06 | 0.75 | 0.62 | 0.63 | 2.32 | 1.50 | 2.04 | 3.76 | 0.44 | 3.34 | 1.21 |
| 3/4 | 4 3/4 | 1.25 | 0.88 | 0.81 | 0.75 | 2.75 | 1.81 | 2.40 | 4.53 | 0.50 | 3.97 | 2.25 |
| 7/8 | 6 1/2 | 1.44 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.88 | 3.20 | 2.10 | 2.86 | 5.33 | 0.50 | 4.5 | 3.16 |
| 1 | 8 1/2 | 1.69 | 1.13 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 3.69 | 2.38 | 3.24 | 5.94 | 0.56 | 5.13 | 4.75 |
| 1 1/8 | 9 1/2 | 1.81 | 1.25 | 1.25 | 1.13 | 4.07 | 2.69 | 3.61 | 6.78 | 0.63 | 5.71 | 6.75 |
| 1 1/4 | 12 | 2.03 | 1.38 | 1.38 | 1.25 | 4.53 | 3.00 | 3.97 | 7.50 | 0.69 | 6.25 | 9.06 |
| 1 3/8 | 13 1/2 | 2.25 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.38 | 5.01 | 3.31 | 4.43 | 8.28 | 0.75 | 6.53 | 11.63 |
| 1 1/2 | 17 | 2.38 | 1.62 | 1.62 | 1.50 | 5.38 | 3.62 | 4.87 | 9.05 | 0.81 | 7.33 | 15.95 |
| 1 3/4 | 25 | 2.88 | 2.12 | 2.12 | 1.75 | 6.38 | 4.19 | 5.78 | 10.97 | 1.00 | 9.06 | 26.75 |
| 2 | 32 | 3.25 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 7.25 | 5.00 | 6.77 | 12.74 | 1.22 | 10.35 | 42.31 |
| 2 1/2 | 55 | 4.12 | 2.62 | 2.63 | 2.63 | 9.38 | 5.68 | 8.07 | 14.85 | 1.38 | 13.00 | 71.75 |
US Type Bow Shackle G2130
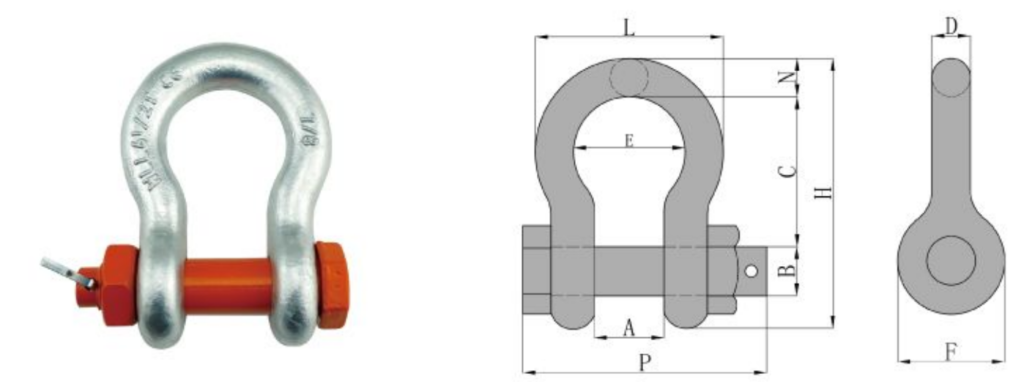
Feature:
- Material: Body 45# Carbon Steel, Pin 40Cr Alloy Steel
- Technology: Drop Forged
- Surface Finish: Electro Galvanized, Hot Dip Galvanized, Dacromet, Powder Coated
- Ultimate Load: 4 times or 6 times of the WILL
- Heat Treatment: 6 times
- WLL: 1/3-150T
- Usage: Lifting and connecting, Wire rope fittings, chain fittings, Maring hardware fittings
Parameters
| Size (in) | WLL (t) | Dimensions(in) | Weight(lbs) | |||||||||
| A | B | C | D | E | F | H | L | N | P | |||
| 3/16 | 1/3 | 0.38 | 0.25 | 0.88 | 0.19 | 0.60 | 0.56 | 1.47 | 0.98 | 0.19 | 1.29 | 0.06 |
| 1/4 | 1/2 | 0.47 | 0.31 | 1.13 | 0.25 | 0.78 | 0.61 | 1.84 | 1.28 | 0.25 | 1.56 | 0.17 |
| 5/16 | 3/4 | 0.53 | 0.38 | 1.22 | 0.31 | 0.84 | 0.75 | 2.09 | 1.47 | 0.31 | 1.82 | 0.22 |
| 3/8 | 1 | 0.66 | 0.44 | 1.44 | 0.38 | 1.03 | 0.91 | 2.49 | 1.78 | 0.38 | 2.17 | 0.33 |
| 7/16 | 1-1/2 | 0.75 | 0.50 | 1.69 | 0.44 | 1.16 | 1.06 | 2.91 | 2.03 | 0.44 | 2.51 | 0.49 |
| 1/2 | 2 | 0.81 | 0.63 | 1.88 | 0.50 | 1.31 | 1.19 | 3.28 | 2.31 | 0.50 | 2.80 | 0.79 |
| 5/8 | 3-1/4 | 1.06 | 0.75 | 2.38 | 0.63 | 1.69 | 1.50 | 4.19 | 2.94 | 0.69 | 3.53 | 1.68 |
| 3/4 | 4-3/4 | 1.25 | 0.88 | 2.81 | 0.75 | 2.00 | 1.81 | 4.97 | 3.50 | 0.81 | 4.07 | 2.72 |
| 7/8 | 6-1/2 | 1.44 | 1.00 | 3.31 | 0.88 | 2.28 | 2.09 | 5.83 | 4.03 | 0.97 | 4.71 | 3.95 |
| 1 | 8-1/2 | 1.69 | 1.13 | 3.75 | 1.00 | 2.69 | 2.38 | 6.56 | 4.96 | 1.06 | 5.31 | 6.12 |
| 1-1/8 | 9-1/2 | 1.81 | 1.25 | 4.25 | 1.13 | 2.91 | 2.69 | 7.47 | 5.16 | 1.25 | 5.09 | 8.27 |
| 1-1/4 | 12 | 2.03 | 1.38 | 4.69 | 1.25 | 3.25 | 3.00 | 8.25 | 5.75 | 1.38 | 6.51 | 11.71 |
| 1-3/8 | 13-1/2 | 2.25 | 1.50 | 5.25 | 1.38 | 3.63 | 3.31 | 9.16 | 6.38 | 1.50 | 7.21 | 15.83 |
| 1-1/2 | 17 | 2.38 | 1.63 | 5.75 | 1.50 | 3.88 | 3.63 | 10.00 | 6.88 | 1.62 | 7.73 | 20.80 |
| 1-3/4 | 25 | 2.88 | 2.00 | 7.00 | 1.75 | 5.00 | 4.19 | 12.34 | 8.86 | 2.25 | 9.05 | 33.91 |
| 2 | 35 | 3.25 | 2.30 | 7.75 | 2.08 | 5.75 | 4.81 | 13.68 | 10.15 | 2.40 | 10.41 | 52.25 |
| 1-1/2 | 55 | 4.13 | 2.80 | 10.50 | 2.71 | 7.25 | 5.69 | 17.90 | 12.75 | 3.13 | 13.56 | 98.25 |
| 3 | 85 | 5.00 | 3.30 | 13.00 | 3.12 | 7.88 | 6.50 | 21.50 | 14.62 | 3.62 | 16.50 | 154.00 |
| 3-1/2 | 120 | 5.25 | 3.76 | 14.63 | 3.62 | 9.00 | 8.00 | 24.88 | 17.02 | 4.38 | 19.00 | 265.00 |
| 4 | 150 | 5.50 | 4.26 | 14.50 | 4.00 | 10.00 | 9.00 | 25.68 | 18.00 | 4.56 | 19.75 | 338.00 |
US Type Dee Shackle G2150
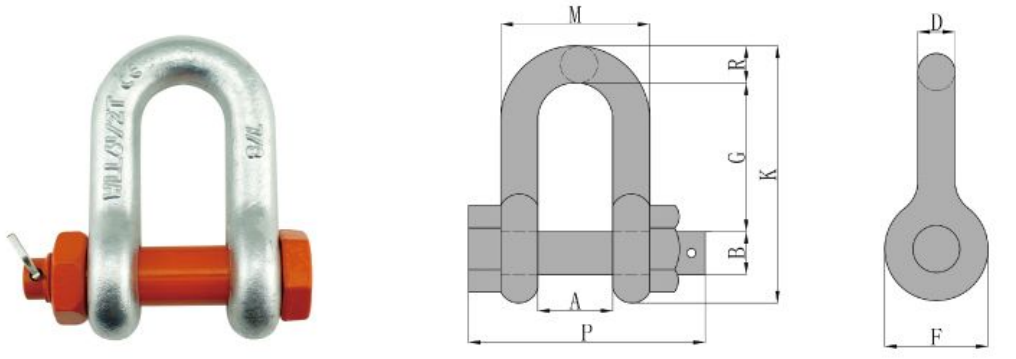
Feature:
- Material: Body 45# Carbon Steel, Pin 40Cr Alloy Steel
- Technology: Drop Forged
- Surface Finish: Electro Galvanized, Hot Dip Galvanized, Dacromet, Powder Coated
- Ultimate Load: 4 times or 6 times of the WILL
- Heat Treatment: 6 times
- WLL: 1/2-55T
- Usage: Lifting and connecting, Wire rope fittings, chain fittings, Maring hardware fitting
Parameters
| Size (in) | WLL (t) | Dimensions(in) | Weight (lbs) | ||||||||
| A | B | D | F | G | K | M | P | R | |||
| 1/4 | 1/2 | 0.47 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.62 | 0.91 | 1.59 | 0.97 | 1.56 | 0.25 | 0.13 |
| 5/16 | 3/4 | 0.53 | 0.38 | 0.31 | 0.75 | 1.07 | 1.91 | 1.15 | 1.82 | 0.31 | 0.23 |
| 3/8 | 1 | 0.66 | 0.44 | 0.38 | 0.92 | 1.28 | 2.31 | 1.42 | 2.17 | 0.38 | 0.33 |
| 7/16 | 1-1/2 | 0.75 | 0.50 | 0.44 | 1.06 | 1.48 | 2.67 | 1.63 | 2.51 | 0.44 | 0.49 |
| 1/2 | 2 | 0.81 | 0.64 | 0.50 | 1.18 | 1.66 | 3.03 | 1.81 | 2.80 | 0.50 | 0.75 |
| 5/8 | 3-1/4 | 1.06 | 0.77 | 0.63 | 1.50 | 2.04 | 3.76 | 2.32 | 3.56 | 0.63 | 1.47 |
| 3/4 | 4-3/4 | 1.25 | 0.89 | 0.75 | 1.81 | 2.40 | 4.53 | 2.75 | 4.15 | 0.81 | 2.52 |
| 7/8 | 6-1/2 | 1.44 | 1.02 | 0.88 | 2.10 | 2.86 | 5.33 | 3.20 | 4.82 | 0.97 | 3.85 |
| 1 | 8-1/2 | 1.69 | 1.15 | 1.00 | 2.38 | 3.24 | 5.94 | 3.69 | 5.39 | 1.00 | 5.55 |
| 1-1/8 | 9-1/2 | 1.81 | 1.25 | 1.13 | 2.68 | 3.61 | 6.78 | 4.07 | 5.90 | 1.25 | 7.60 |
| 1-1/4 | 12 | 2.03 | 1.40 | 1.25 | 3.00 | 3.97 | 7.50 | 4.53 | 6.69 | 1.38 | 10.81 |
| 1-3/8 | 13-1/2 | 2.25 | 1.53 | 1.38 | 3.31 | 4.43 | 8.28 | 5.01 | 7.21 | 1.50 | 13.75 |
| 1-1/2 | 17 | 2.38 | 1.66 | 1.50 | 3.62 | 4.87 | 9.05 | 5.38 | 7.73 | 1.62 | 18.50 |
| 1-3/4 | 25 | 2.88 | 2.04 | 1.75 | 4.19 | 5.82 | 10.97 | 6.38 | 9.33 | 2.21 | 31.4 |
| 2 | 35 | 3.25 | 2.30 | 2.10 | 5.00 | 6.82 | 12.74 | 7.25 | 10.41 | 2.36 | 46.75 |
| 1-1/2 | 55 | 4.12 | 2.80 | 2.63 | 5.68 | 8.07 | 14.85 | 9.38 | 13.58 | 2.63 | 85.00 |
| 3 | 85 | 5.00 | 3.25 | 3.00 | 6.50 | 8.56 | 16.87 | 11.00 | 15.13 | 3.50 | 124.25 |
European Type Dee Shackle
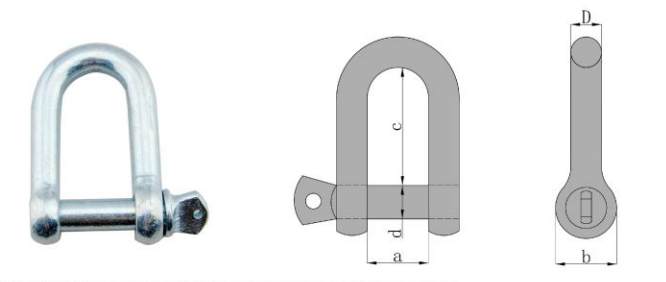
Feature:
- Material: Q235 Carbon Steel
- Technology: Free Forged
- Surface Finish: Electro Galvanized
- WLL: 80-8000KG
- Usage: Lifting and connecting, Wire rope fittings, chain fittings, Maring hardware fittings
Parameters
| Size(D) (mm) | WLL (kg) | Dimensions(mm) | Weight (kg) | |||
| d | a | c | b | |||
| 6 | 100 | 6 | 13 | 25 | 14 | 0.023 |
| 8 | 200 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 18 | 0.048 |
| 10 | 320 | 10 | 19 | 38 | 20 | 0.085 |
| 12 | 520 | 12 | 25 | 51 | 26 | 0.17 |
| 16 | 800 | 16 | 32 | 64 | 33 | 0.385 |
| 20 | 1100 | 20 | 38 | 76 | 40 | 0.76 |
| 22 | 1500 | 22 | 44 | 89 | 50 | 1.07 |
| 25 | 2100 | 25 | 51 | 100 | 57 | 1.55 |
| 28 | 3000 | 28 | 57 | 115 | 68 | 2.25 |
| 32 | 3500 | 32 | 64 | 127 | 73 | 3.35 |
| 38 | 5000 | 38 | 76 | 152 | 85 | 5.85 |
| 45 | 7000 | 45 | 90 | 180 | 96 | 10 |
| 50 | 8000 | 50 | 102 | 200 | 108 | 12.5 |
European Type Bow Shackle

Feature:
Material : Q235 Carbon Steel
Technology: Free Forged
Surface Finish: Electro Galvanized
WLL: 80-8000KG
Usage: Lifting and connecting, Wire rope fittings, chain fittings, Maring hardware fittings
Parameters
| WLL (kg) | Size(D) (mm) | WLL (kg) | Dimensions(mm) | Weight (kg) | ||||
| d | a | c | r | b | ||||
| 80 | 5 | 80 | 5 | 10 | 19 | 8 | 11 | 0.016 |
| 100 | 6 | 100 | 6 | 13 | 25 | 10 | 14 | 0.024 |
| 200 | 8 | 200 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 12 | 18 | 0.050 |
| 320 | 10 | 320 | 10 | 19 | 38 | 16 | 20 | 0.088 |
| 520 | 12 | 520 | 12 | 25 | 51 | 19 | 26 | 0.180 |
| 800 | 16 | 800 | 16 | 32 | 64 | 28 | 33 | 0.410 |
| 1100 | 20 | 1100 | 20 | 38 | 76 | 33 | 40 | 0.776 |
| 1500 | 22 | 1500 | 22 | 44 | 89 | 37 | 50 | 1.150 |
| 2100 | 25 | 2100 | 25 | 51 | 100 | 40 | 57 | 1.650 |
| 3000 | 28 | 3000 | 28 | 57 | 115 | 47 | 68 | 2.400 |
| 3500 | 32 | 3500 | 32 | 64 | 127 | 52 | 73 | 3.500 |
| 5000 | 38 | 5000 | 38 | 76 | 152 | 63 | 85 | 6.350 |
| 7000 | 45 | 7000 | 45 | 90 | 180 | 75 | 96 | 11.500 |
| 8000 | 50 | 8000 | 50 | 102 | 200 | 78 | 108 | 14.000 |
JIS Type Dee Shackle

Feature:
- Material: Q235 Carbon Steel
- Technology: Free Forged
- Surface Finish: Electro Galvanized
- Usage: Lifting and connecting, Wire rope fittings, chain fittings, Maring hardware fittings
Parameters
| Size | Dimensions(mm) | WLL(t) | Weight(kg) | ||||
| m/m | in | B | D | L | d1 | ||
| 5 | 3/16 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 18.50 | 5.00 | 0.09 | 0.013 |
| 6 | 1/4 | 12.00 | 11.00 | 25.00 | 6.50 | 0.15 | 0.026 |
| 8 | 5/16 | 14.00 | 15.00 | 31.00 | 8.50 | 0.25 | 0.046 |
| 9 | 3/8 | 18.00 | 17.00 | 36.00 | 10.00 | 0.40 | 0.070 |
| 12 | 1/2 | 24.00 | 23.00 | 46.00 | 13.00 | 0.60 | 0.170 |
| 16 | 5/8 | 30.00 | 32.00 | 59.00 | 17.00 | 0.80 | 0.400 |
| 19 | 3/1 | 36.00 | 37.00 | 74.00 | 20.00 | 1.00 | 0.700 |
| 22 | 7/8 | 43.00 | 43.00 | 86.00 | 23.00 | 1.50 | 1.100 |
| 25 | 1 | 47.00 | 50.00 | 95.00 | 27.00 | 2.00 | 1.700 |
| 28 | 11/8 | 55.00 | 56.00 | 110.00 | 30.00 | 2.50 | 2.400 |
| 32 | 11/4 | 64.00 | 64.00 | 130.00 | 34.00 | 3.20 | 3.600 |
| 38 | 11/2 | 76.00 | 76.00 | 145.00 | 40.00 | 4.20 | 6.000 |
| 44 | 13/4 | 80.00 | 90.00 | 160.00 | 47.00 | 6.50 | 10.000 |
| 50 | 2 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 185.00 | 53.00 | 8.00 | 12.000 |
| 65 | 21/2 | 110.00 | 130.00 | 240.00 | 68.00 | 15.00 | 28.000 |
| 75 | 3 | 120.00 | 150.00 | 300.00 | 78.00 | 20.00 | 44.000 |
JIS Type Dee Shackle Without Collor
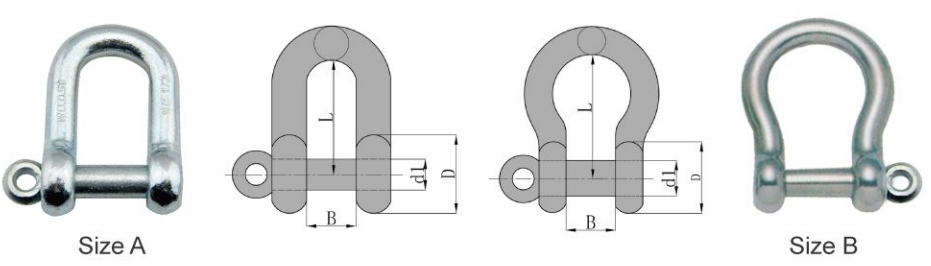
Feature:
- Material: Q235 Carbon Steel
- Technology: Free Forged
- Surface Finish: Electro Galvanized
- Usage: Lifting and connecting, Wire rope fittings, chain fittings, Maring hardware fittings
Parameters
| Size | Dimensions(mm) | WLL(t) | Weight(kg) | |||||
| m/m | in | B | D | L | d1 | A | B | |
| 5 | 3/16 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 18.50 | 5.00 | 0.09 | 0.013 | 0.024 |
| 6 | 1/4 | 12.00 | 11.00 | 25.00 | 6.50 | 0.15 | 0.026 | 0.062 |
| 8 | 5/16 | 14.00 | 15.00 | 31.00 | 8.50 | 0.25 | 0.046 | 0.062 |
| 9 | 3/8 | 18.00 | 17.00 | 36.00 | 10.00 | 0.40 | 0.070 | 0.077 |
| 12 | 1/2 | 24.00 | 23.00 | 46.00 | 13.00 | 0.60 | 0.170 | 0.190 |
| 16 | 5/8 | 30.00 | 32.00 | 59.00 | 17.00 | 0.80 | 0.400 | 0.475 |
| 19 | 3/1 | 36.00 | 37.00 | 74.00 | 20.00 | 1.00 | 0.700 | 0.780 |
| 22 | 7/8 | 43.00 | 43.00 | 86.00 | 23.00 | 1.50 | 1.100 | 1.180 |
| 25 | 1 | 47.00 | 50.00 | 95.00 | 27.00 | 2.00 | 1.700 | 1.800 |
| 28 | 11/8 | 55.00 | 56.00 | 110.00 | 30.00 | 2.50 | 2.400 | 2.550 |
| 32 | 11/4 | 64.00 | 64.00 | 130.00 | 34.00 | 3.20 | 3.600 | 3.900 |
| 38 | 11/2 | 76.00 | 76.00 | 145.00 | 40.00 | 4.20 | 6.000 | 6.900 |
| 44 | 13/4 | 80.00 | 90.00 | 160.00 | 47.00 | 6.50 | 10.000 | — |
| 50 | 2 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 185.00 | 53.00 | 8.00 | 12.000 | — |
| 65 | 21/2 | 110.00 | 130.00 | 240.00 | 68.00 | 15.00 | 28.000 | — |
| 75 | 3 | 120.00 | 150.00 | 300.00 | 78.00 | 20.00 | 44.000 | — |
BS3032 Bow Shackle
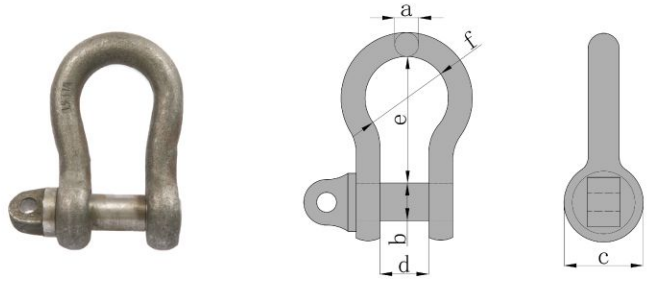
Feature:
- Standard: British Standard
- Material: 45# Carbon Steel
- Technology: Free Forged
- Surface Finish: Electro Galvanized
- Application: Lifting
Parameters
| WLL(t) | Dimensions(mm) | Weight (kg) | |||||
| a | b | c | d | e | f | ||
| 0.15 | 6.00 | 10.00 | 19.00 | 13.00 | 28.00 | 19.00 | 0.12 |
| 0.45 | 10.00 | 13.00 | 25.00 | 16.00 | 41.00 | 25.00 | 0.18 |
| 0.75 | 13.00 | 16.00 | 32.00 | 22.00 | 54.00 | 32.00 | 0.37 |
| 1.25 | 16.00 | 19.00 | 38.00 | 28.00 | 70.00 | 41.00 | 0.72 |
| 2.00 | 19.00 | 22.00 | 44.00 | 35.00 | 86.00 | 51.00 | 1.20 |
| 2.75 | 22.00 | 25.20 | 50.00 | 41.00 | 98.00 | 57.00 | 1.85 |
| 3.75 | 25.00 | 28.30 | 56.00 | 45.00 | 108.00 | 64.00 | 2.61 |
| 4.75 | 28.00 | 31.70 | 63.00 | 51.00 | 124.00 | 73.00 | 3.78 |
| 5.75 | 32.00 | 35.00 | 70.00 | 57.00 | 137.00 | 83.00 | 5.17 |
| 7.25 | 35.00 | 38.00 | 75.00 | 63.00 | 152.00 | 89.00 | 6.46 |
| 8.50 | 38.00 | 43.00 | 89.00 | 70.00 | 168.00 | 98.00 | 8.34 |
| 9.50 | 42.00 | 48.00 | 89.00 | 76.00 | 187.00 | 111.00 | 11.10 |
| 11.50 | 44.00 | 51.00 | 95.00 | 86.00 | 206.00 | 121.00 | 14.50 |
| 13.00 | 48.00 | 54.00 | 106.00 | 92.00 | 222.00 | 130.00 | 17.80 |
| 15.00 | 51.00 | 57.00 | 114.00 | 98.00 | 238.00 | 140.00 | 25.50 |
| 18.50 | 57.00 | 60.00 | 124.00 | 105.00 | 257.00 | 152.00 | 34.40 |
| 20.00 | 60.00 | 64.00 | 127.00 | 111.00 | 273.00 | 162.00 | 36.80 |
| 25.00 | 67.00 | 73.00 | 148.00 | 121.00 | 302.00 | 178.00 | 45.00 |
| 30.00 | 73.00 | 79.00 | 150.00 | 133.00 | 330.00 | 197.00 | 62.20 |
| 35.00 | 79.00 | 86.00 | 171.00 | 146.00 | 359.00 | 213.00 | 81.80 |
| 40.00 | 85.00 | 89.00 | 178.00 | 159.00 | 387.00 | 229.00 | 95.00 |
| 50.00 | 95.00 | 102.00 | 203.00 | 171.00 | 429.00 | 254.00 | 131.00 |
| 65.00 | 108.00 | 114.00 | 229.00 | 197.00 | 483.00 | 286.00 | 194.00 |
| 80.00 | 117.00 | 127.00 | 254.00 | 216.00 | 533.00 | 308.00 | 274.00 |
BS3032 Dee Shackle

Feature:
- Standard: British Standard
- Material: 45# Carbon Steel
- Technology: Free Forged
- Surface Finish: Electro Galvanized
- Application: Lifting
Parameters
| WLL(t) | Dimensions(mm) | Weight (kg) | ||||
| a | b | c | d | e | ||
| 0.25 | 6.00 | 10.00 | 19.00 | 13.00 | 25.00 | 0.11 |
| 0.50 | 10.00 | 13.00 | 25.00 | 19.00 | 38.00 | 0.17 |
| 0.75 | 13.00 | 16.00 | 32.00 | 26.00 | 54.00 | 0.35 |
| 1.50 | 16.00 | 19.00 | 38.00 | 32.00 | 64.00 | 0.68 |
| 2.00 | 19.00 | 22.00 | 44.00 | 38.00 | 73.00 | 1.02 |
| 3.00 | 22.00 | 25.20 | 50.00 | 44.00 | 82.00 | 1.57 |
| 3.75 | 25.00 | 28.30 | 56.00 | 51.00 | 95.00 | 2.30 |
| 5.00 | 28.00 | 31.70 | 63.00 | 54.00 | 105.00 | 3.20 |
| 6.00 | 32.00 | 35.00 | 70.00 | 60.00 | 114.00 | 4.30 |
| 7.00 | 35.00 | 38.00 | 75.00 | 67.00 | 127.00 | 5.40 |
| 9.50 | 38.00 | 43.00 | 89.00 | 70.00 | 137.00 | 6.80 |
| 11.25 | 42.00 | 48.00 | 89.00 | 76.00 | 146.00 | 8.70 |
| 13.00 | 44.00 | 51.00 | 95.00 | 83.00 | 156.00 | 11.00 |
| 14.00 | 48.00 | 54.00 | 106.00 | 92.00 | 178.00 | 14.30 |
| 16.00 | 51.00 | 57.00 | 114.00 | 98.00 | 187.00 | 20.00 |
| 18.00 | 54.00 | 60.00 | 124.00 | 105.00 | 197.00 | 26.40 |
| 20.00 | 57.00 | 64.00 | 127.00 | 108.00 | 210.00 | 28.30 |
| 25.00 | 64.00 | 73.00 | 148.00 | 121.00 | 235.00 | 36.00 |
| 30.00 | 70.00 | 79.00 | 150.00 | 123.00 | 260.00 | 40.00 |
| 35.00 | 76.00 | 86.00 | 171.00 | 146.00 | 279.00 | 63.60 |
| 40.00 | 79.00 | 89.00 | 178.00 | 149.00 | 292.00 | 71.70 |
| 50.00 | 89.00 | 102.00 | 203.00 | 171.00 | 330.00 | 101.00 |
| 65.00 | 102.00 | 114.00 | 229.00 | 181.00 | 275.00 | 151.00 |
| 80.00 | 114.00 | 127.00 | 254.00 | 219.00 | 419.00 | 215.00 |
Commerical Shackle
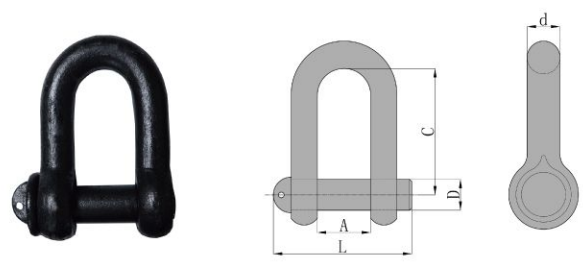
Feature:
- Material: Q235 Carbon Steel
- Technology: Free Forged
- Surface Finish: 0.2T-3.3T Zinc Plated; 4.1T-21T Black Painted
- Application: Lifting
Parameters
| Size (t) | Working Load Limit (kg) | D(mm) | d(mm) | A(mm) | C(mm) | L(mm) |
| 0.20 | 196 | M8 | 6 | 12 | 35 | 35 |
| 0.30 | 324 | M10 | 8 | 16 | 45 | 44 |
| 0.50 | 490 | M12 | 10 | 20 | 50 | 55 |
| 0.90 | 912 | M16 | 12 | 24 | 60 | 65 |
| 1.40 | 1420 | M20 | 16 | 32 | 80 | 86 |
| 2.10 | 2060 | M24 | 20 | 36 | 90 | 101 |
| 2.70 | 2650 | M27 | 22 | 40 | 100 | 111 |
| 3.30 | 3240 | M30 | 24 | 45 | 110 | 123 |
| 4.10 | 4020 | M33 | 27 | 50 | 120 | 137 |
| 4.90 | 4810 | M36 | 30 | 58 | 130 | 153 |
| 6.80 | 6670 | M42 | 36 | 64 | 150 | 176 |
| 9.00 | 8830 | M48 | 42 | 70 | 170 | 197 |
| 10.70 | 10500 | M52 | 45 | 80 | 190 | 218 |
| 16.00 | 15700 | M64 | 52 | 99 | 235 | 262 |
| 21.00 | 20600 | M76 | 65 | 100 | 256 | 321 |
Your Ultimate Guide to Acquiring Shackle
Shackles are essential components in various industries, including construction, marine, and transportation. They are used to connect different lifting devices, provide secure attachment points, and ensure the safety and efficiency of operations. This guide will help you understand the different types of shackles, their applications, and key factors to consider when acquiring them.
Table of contents
Chapt 1
What is a shackle and what are its main types?
A shackle is a U-shaped metal connector used to secure lifting slings, chains, ropes, and other rigging equipment to loads and lifting devices. It is an essential component in lifting, rigging, and material handling operations, providing a secure and reliable connection point. The shackle consists of a body and a pin or bolt that can be secured across the opening.
Main Types of Shackles
1. Anchor Shackles (Bow Shackles):
Design: U-shaped with a larger, rounded “bow” and a removable pin.
Applications: Suitable for applications requiring multidirectional load handling. Commonly used in situations where slings or multiple connections might need to be accommodated.
Advantages: The larger bow shape allows for multiple slings to be connected and provides flexibility in rigging configurations.
Typical Uses: Lifting, rigging, towing, and heavy-duty applications where flexibility is required.
2. Chain Shackles (D Shackles):
Design: D-shaped with a straight, narrower body and a removable pin.
Applications: Ideal for straight-line pulls and single connection points. Commonly used in connecting chains to other lifting components.
Advantages: Provides higher strength for straight-line loads due to its narrower design.
Typical Uses: Securing loads, connecting chain to lifting equipment, and applications where the load is in a straight line.
Pin Types
1. Screw Pin:
Design: A pin that screws into the shackle body.
Applications: Suitable for applications where the pin needs to be removed frequently.
Advantages: Easy to use and quick to remove.
Typical Uses: Temporary connections, fieldwork, and situations requiring quick assembly and disassembly.
2. Bolt Type (Safety Pin):
Design: A pin secured with a nut and cotter pin.
Applications: Used in permanent or long-term installations where safety and security are paramount.
Advantages: Provides a more secure connection, preventing accidental removal.
Typical Uses: Permanent installations, critical load-bearing applications, and environments where vibration might cause a screw pin to loosen.
3. Round Pin:
Design: A straight pin secured by a cotter pin.
Applications: Used in applications where the load is primarily in-line and minimal side load is present.
Advantages: Simple design, easy to assemble and disassemble.
Typical Uses: Marine applications, trawling, and sailing.
Key Considerations for Acquiring Shackles
1. Load Capacity:
Working Load Limit (WLL): Ensure the shackle can handle the maximum expected load. The WLL should always be clearly marked on the shackle.
Safety Factor: Commonly 5:1 or 6:1, meaning the breaking strength is five or six times the WLL.
2. Material:
Stainless Steel: Resistant to corrosion, ideal for marine and corrosive environments.
Galvanized Steel: Cost-effective with moderate corrosion resistance.
Alloy Steel: High strength, suitable for heavy-duty applications.
3. Certifications and Standards:
Ensure the shackles meet industry standards such as ASME B30.26, EN 13889, or ASTM A153. Certification from recognized bodies ensures reliability and safety.
Environmental Conditions:
Consider factors like temperature, humidity, and exposure to chemicals. Select materials and coatings accordingly to ensure longevity and safety.
4. Manufacturer Reputation:
Choose reputable manufacturers with a history of producing high-quality shackles. Look for reviews, testimonials, and compliance with international standards.
By understanding the different types of shackles and their specific applications, you can ensure the safety and efficiency of your lifting and rigging operations. Regular maintenance and adherence to industry standards will help in maintaining the reliability of the shackles used in your operations.
Chapt 2
How do you identify the different parts of a shackle?
The Parts of a Shackle:
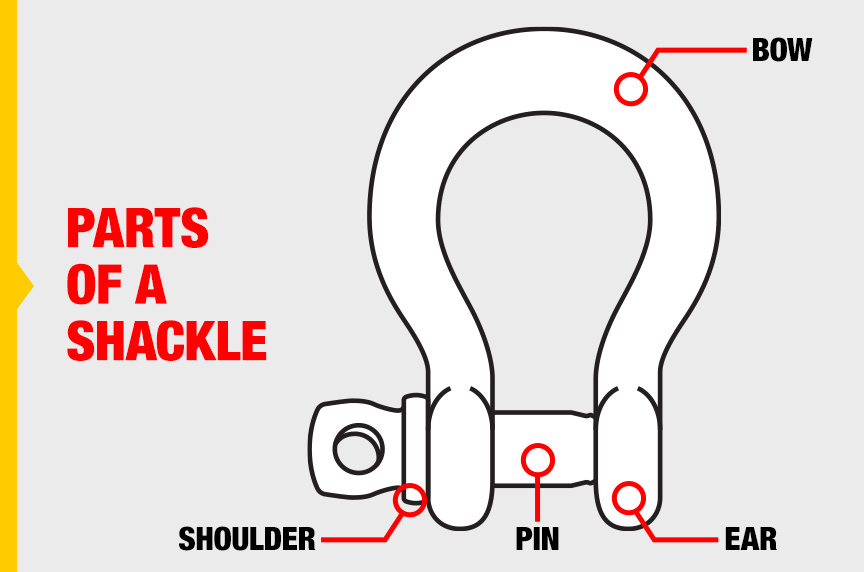
Before we begin, let’s identify the different parts of a shackle so when we use terms like “bow,” “ears,” “pin,” or “shoulder,” you’re familiar with what we’re referring to:
- Bow – the curved portion of the shackle body opposite the pin—often referred to as the bail, body, dee, or bowl
- Ears – portion of the shackle body that support the shackle pin
- Pin – a steel bolt made to span the two shackle ears
- Shoulder – the part of the pin that makes contact against the ear when the pin is fully threaded or engaged
Identifying the Different Parts of a Shackle
A shackle is composed of several key parts, each serving a specific function to ensure secure and efficient operation in lifting and rigging tasks. Here’s a breakdown of the different parts of a shackle and how to identify them:
Body (Bow or Dee)
Description: The main U-shaped or D-shaped component of the shackle.
Types:
Bow (Anchor) Shackle: Features a larger, rounded shape, allowing for multi-directional load handling.
Dee (Chain) Shackle: Has a more narrow, straight-sided design, ideal for straight-line pulls.
Identification: Look for the overall shape of the shackle. Bow shackles are more rounded, while Dee shackles have straight sides.
Pin (Bolt or Screw Pin)
Description: The component that secures the open end of the shackle body, allowing for connection to other components.
Types:
Screw Pin: A threaded pin that screws into the body of the shackle.
Bolt Type (Safety Pin): A pin secured with a nut and a cotter pin for added security.
Round Pin: A straight pin that is secured with a cotter pin.
Identification: Examine how the pin is secured:
Screw Pin: Easily identifiable by its threaded end.
Bolt Type: Recognized by the presence of a nut and cotter pin.
Round Pin: Identified by its straight, smooth design with a cotter pin.
Shoulder
Description: The part of the shackle body that the pin fits into, ensuring proper alignment and load distribution.
Identification: Located at the end of the shackle body where the pin is inserted. It may have a flat or slightly rounded surface to accommodate the pin.
Ears (Eyes)
Description: The extended arms of the shackle body that house the pin holes.
Identification: The two ends of the shackle that form the opening, where the pin passes through to secure the shackle. They are opposite the bow in an anchor shackle and opposite the straight side in a chain shackle.
Pin Hole
Description: The holes in the ears through which the pin is inserted.
Identification: Located on the ends of the shackle body’s ears. The size and threading (if any) will match the corresponding pin.
Visual Guide to Shackle Parts
Body (Bow or Dee)
Shape: Rounded (Bow Shackle) or D-shaped (Dee Shackle).
Function: Provides the main structure and load-bearing capacity.
Pin (Bolt or Screw Pin)
Shape: Cylindrical with threading (Screw Pin) or a smooth pin with a cotter hole (Round Pin).
Function: Secures the shackle, allowing for connection to other components.
Shoulder
Shape: Flat or slightly rounded surface adjacent to the pin holes.
Function: Ensures proper pin alignment and load distribution.
Ears (Eyes)
Shape: Extended arms forming the U or D shape of the shackle with holes for the pin.
Function: Houses the pin, securing the shackle.
Pin Hole
Shape: Circular openings in the ears.
Function: Allows the pin to be inserted and secured, completing the shackle.
By familiarizing yourself with these parts and their functions, you can accurately identify and select the appropriate shackle for your specific lifting and rigging needs, ensuring safety and efficiency in your operations.


Chapt 3
What materials are shackles typically made from?
Materials Used in Shackles
Shackles are typically made from robust and durable materials to ensure they can handle heavy loads and withstand harsh environments. Here are the most common materials used in shackle manufacturing:
Stainless Steel
Properties: Highly resistant to corrosion and rust, durable, and strong.
Applications: Ideal for marine environments, chemical plants, and food processing industries where exposure to corrosive elements is common.
Advantages: Long-lasting, requires minimal maintenance, and retains strength in harsh conditions.
Disadvantages: More expensive than other materials.Galvanized Steel
Properties: Steel that has been coated with a layer of zinc to prevent corrosion.
Applications: Suitable for general-purpose use, including construction, outdoor environments, and industrial applications.
Advantages: Cost-effective, provides good corrosion resistance, widely available.
Disadvantages: The zinc coating can wear off over time, reducing corrosion resistance.
Alloy Steel
Properties: A mixture of steel and other elements (such as chromium, molybdenum, and nickel) to enhance strength and toughness.
Applications: Heavy-duty lifting, rigging, and towing operations where high strength and durability are required.
Advantages: High strength-to-weight ratio, excellent durability, able to handle high-stress applications.
Disadvantages: Can be more expensive than regular carbon steel.Carbon Steel
Properties: Composed mainly of iron and carbon, providing good strength and durability.
Applications: Used in general-purpose shackles for construction, transportation, and industrial applications.
Advantages: Strong, durable, and cost-effective.
Disadvantages: Susceptible to rust and corrosion if not properly treated or coated.
Comparison of Materials
Material | Corrosion Resistance | Strength | Durability | Cost | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Stainless Steel | Excellent | High | Very high | High | Marine, chemical plants, food processing |
Galvanized Steel | Good | Moderate | Good | Moderate | Construction, outdoor, general industrial use |
Alloy Steel | Moderate | Very High | High | High | Heavy-duty lifting, rigging, towing |
Carbon Steel | Low | High | Good | Low to Moderate | General-purpose construction, transportation |
Selecting the Right Material
When choosing a shackle, consider the following factors to determine the appropriate material:
Environmental Conditions:
For corrosive environments (e.g., marine or chemical), stainless steel is the best choice due to its high corrosion resistance.
For general outdoor use, galvanized steel offers a good balance of corrosion resistance and cost.Load Requirements:
For heavy-duty applications, alloy steel shackles provide the necessary strength and durability.
For lighter loads or less critical applications, carbon steel shackles are often sufficient and more cost-effective.Budget:
Stainless steel and alloy steel are more expensive but offer superior performance and longevity.
Galvanized and carbon steel are more economical choices for general applications.
By understanding the properties and advantages of each material, you can select the most suitable shackle for your specific needs, ensuring safety, performance, and cost-effectiveness in your operations.
Chapt 4
How do you determine the working load limit (WLL) of a shackle?
Determining the Working Load Limit (WLL) of a Shackle
The Working Load Limit (WLL) is the maximum load that a shackle can safely handle during operation. It is a critical factor in ensuring safety and effectiveness in lifting and rigging applications. Here’s how to determine the WLL of a shackle:
1. Manufacturer’s Specifications
Check the Markings: Reputable manufacturers typically mark the WLL directly on the shackle body. This information is often stamped or engraved.
Consult Manufacturer Documentation: Manufacturer catalogs, datasheets, or user manuals will provide the WLL along with other specifications.
2. Standards and Certification
Industry Standards: Shackles are manufactured to comply with industry standards such as ASME B30.26, EN 13889, or ASTM A153. These standards specify the required safety factors and testing methods to determine the WLL.
Third-Party Certification: Certified shackles have undergone rigorous testing and verification by third-party organizations to ensure they meet the specified WLL.
3. Material and Design
Material Strength: The WLL depends on the material used in the shackle’s construction. High-strength materials like alloy steel typically have higher WLLs compared to carbon steel or galvanized steel.
Shackle Design: The design of the shackle, including its shape (anchor/bow or chain/D shackle), affects its load-bearing capacity. Bow shackles can handle multi-directional loads, while chain shackles are optimized for straight-line loads.
4. Safety Factor
Definition: The safety factor is the ratio between the breaking strength of the shackle and its WLL. Common safety factors are 5:1 or 6:1.
Calculation: If the breaking strength of a shackle is known, the WLL can be calculated by dividing the breaking strength by the safety factor.
Example Calculation
Determine Breaking Strength: Assume a shackle has a breaking strength of 30,000 pounds.
Choose Safety Factor: For most lifting applications, a safety factor of 5:1 is used
5. Inspection and Maintenance
Regular Inspection: Inspect shackles regularly for signs of wear, deformation, or damage. A shackle in good condition will perform according to its rated WLL.
Replacement: Replace any shackle that shows signs of wear or damage, as this can reduce its effective WLL.
Summary
To determine the WLL of a shackle:
Check Manufacturer Markings and Documentation: Reliable and precise source of information.
Verify Compliance with Industry Standards: Ensures the shackle has been tested and rated accurately.
Consider Material and Design: Influences load-bearing capacity.
Apply the Safety Factor: Ensures a margin of safety in load calculations.
Perform Regular Inspections: Maintains shackle integrity and reliability.
By following these steps, you can ensure that the shackles used in your operations are both safe and effective for their intended loads.
Chapt 5
What are the safety precautions when using shackles?
Safety Precautions When Using Shackles
Using shackles correctly is crucial to ensure safety and efficiency in lifting and rigging operations. Here are key safety precautions to follow:
1. Selection of Shackles
Correct Type: Choose the appropriate type of shackle (anchor/bow or chain/D) for your specific application.
Load Capacity: Ensure the shackle’s Working Load Limit (WLL) is adequate for the intended load. Do not exceed the WLL.
Material: Select the right material for the environment (e.g., stainless steel for marine environments).
2. Inspection Before Use
Visual Inspection: Check for any visible signs of wear, corrosion, deformation, or cracks. Inspect the pin for damage or wear.
Certification: Use only shackles that have been certified and tested according to industry standards.
3. Proper Assembly
Pin Installation: Ensure the pin is properly seated and secured. For screw pin shackles, make sure the pin is fully threaded and tightened. For bolt-type shackles, ensure the nut and cotter pin are securely in place.
Avoid Side Loading: Shackles are designed for in-line loading. Avoid side loading, which can reduce the shackle’s load capacity and cause failure.
4. Correct Usage
Right Angle: Ensure the shackle is loaded in-line and not at an angle. For bow shackles, loading at an angle can cause unequal stress distribution.
Avoid Overloading: Do not exceed the shackle’s WLL. Factor in dynamic loads and potential shock loading.
Use with Compatible Hardware: Ensure that the diameter of the pin matches the eye of the connecting hardware. The hardware should move freely within the shackle’s bow.
5. Maintenance and Storage
Regular Maintenance: Clean shackles regularly to prevent dirt and corrosion. Lubricate the threads of the pin to ensure smooth operation.
Proper Storage: Store shackles in a dry, clean environment to prevent rust and corrosion. Avoid storing in direct sunlight or extreme temperatures.
6. Operational Precautions
Avoid Sudden Loads: Apply loads gradually to avoid shock loading, which can exceed the WLL.
Temperature Considerations: Be aware of the operational temperature range of the shackle. Extreme temperatures can affect the material’s strength.
Rigging Practices: Use shackles in combination with other rigging hardware correctly. Ensure the entire rigging setup is secure and balanced.
7. Training and Compliance
Qualified Personnel: Ensure that only trained and qualified personnel are handling and inspecting shackles.
Adhere to Regulations: Follow all relevant industry standards and regulations, such as OSHA guidelines and ASME B30.26 for rigging hardware.
Summary of Safety Precautions
Selection:
Choose the correct type and material.
Ensure adequate WLL.
Inspection:
Perform visual checks.
Use certified shackles.
- Assembly:
Properly secure the pin.
Avoid side loading.
- Usage:
Load in-line.
Avoid overloading.
Use compatible hardware.
- Maintenance:
Regular cleaning and lubrication.
Proper storage.
- Operations:
Avoid sudden loads.
Consider temperature effects.
Use proper rigging practices.
- Training:
Qualified personnel.
Adherence to standards.
By following these safety precautions, you can ensure the safe and effective use of shackles in your lifting and rigging operations.
Chapt 6
How do you inspect a shackle for damage or wear?
Inspecting a Shackle for Damage or Wear
Regular inspection of shackles is critical to ensure their safety and reliability in lifting and rigging operations. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to inspect a shackle for damage or wear:
1. Visual Inspection
Surface Condition:
Check for Corrosion: Look for any signs of rust or corrosion, especially in marine or harsh environments. Corrosion can weaken the shackle.
Look for Cracks or Fractures: Inspect the entire shackle for any visible cracks, fractures, or significant wear, especially around the pin holes and the bow.
Examine for Deformation: Ensure the shackle retains its original shape. Look for any bending, elongation, or distortion in the shackle body or pin.
2. Pin Inspection
Thread Condition:
Screw Pin: Check the threads on both the pin and the shackle body for signs of wear, galling, or damage. Ensure the threads are clean and well-lubricated.
Bolt Type: Ensure the nut threads smoothly and the cotter pin is in place and undamaged.
Pin Straightness:
Check for Bends: Ensure the pin is straight and not bent or distorted. A bent pin can indicate overloading or misuse.
Seating and Fit:
Proper Fit: Make sure the pin fits properly into the shackle body and that it can be fully tightened. There should be no excessive play or looseness.
3. Load Bearing Areas
Bow and Ears:
Wear and Tear: Inspect the bow (the rounded part) and the ears (the arms) for signs of excessive wear, gouges, or abrasion.
Pin Holes: Check the pin holes for elongation or deformation, which can weaken the shackle.
4. Measurement Check
Dimensions:
Compare to Manufacturer Specs: Measure the critical dimensions of the shackle (e.g., diameter of the bow, thickness of the pin, width between the ears) and compare them to the original manufacturer’s specifications. Wear should not exceed 10% of the original dimension.
5. Functional Test
Operational Check:
Thread Engagement: For screw pin shackles, ensure the pin screws in smoothly and fully engages without cross-threading.
Locking Mechanism: For bolt-type shackles, ensure the nut can be securely fastened and the cotter pin is in place.
6. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
Advanced Inspection Techniques:
Magnetic Particle Inspection (MPI): Used to detect surface and slightly subsurface discontinuities in ferromagnetic materials.
Ultrasonic Testing (UT): Used to detect internal defects such as cracks or voids.
Dye Penetrant Inspection (DPI): Used to detect surface-breaking defects.
Summary of Inspection Steps
Visual Inspection:
Check for corrosion, cracks, and deformation.
Pin Inspection:
Examine threads, straightness, and proper fit.
Load Bearing Areas:
Inspect the bow, ears, and pin holes for wear and tear.
Measurement Check:
Measure dimensions and compare with manufacturer specs.
Functional Test:
Ensure smooth operation and secure locking.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT):
Use advanced techniques for detailed inspection if needed.
By following these inspection steps, you can identify potential issues early and ensure that your shackles remain safe and reliable for use in lifting and rigging operations. Regular inspection and maintenance are crucial to prevent accidents and equipment failure.
Chapt 7
Screw pin shackle VS a bolt-type shackle?
Shackles are vital components in lifting, rigging, and material handling applications, and they come in different types depending on their pin configuration. The two most common types are screw pin shackles and bolt-type shackles. Here’s a detailed comparison:
1. Screw Pin Shackle
Design:
Pin Configuration: Features a pin with threaded ends that screw into the shackle body.
Ease of Use: The pin is easy to remove and install, making it suitable for applications where frequent assembly and disassembly are required.
Applications:
Temporary Connections: Ideal for temporary rigging setups where the shackle needs to be frequently attached and detached.
Field Use: Commonly used in field operations where quick and easy pin removal is beneficial.
Advantages:
Convenience: Quick to install and remove without the need for additional tools.
Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of applications due to its ease of use.
Disadvantages:
Risk of Unintended Removal: The pin can potentially unscrew under vibration or movement if not properly secured.
Not Ideal for Permanent or Long-Term Installations: Better suited for temporary setups.
2. Bolt-Type Shackle
Design:
Pin Configuration: Consists of a pin secured with a nut and a cotter pin or safety pin. The nut threads onto the pin, and the cotter pin locks the nut in place.
Secure Fit: The combination of the nut and cotter pin provides a more secure and stable connection.
Applications:
Permanent or Long-Term Installations: Suitable for applications where the shackle will remain in place for extended periods.
Critical Load Applications: Used in situations where a secure connection is critical, and there is a risk of the pin coming loose.
Advantages:
Enhanced Security: The nut and cotter pin prevent the pin from accidentally unscrewing, even under vibration.
Reliability: Provides a more reliable and secure connection, suitable for high-stress and critical load applications.
Disadvantages:
Time-Consuming Installation: Takes longer to install and remove compared to a screw pin shackle, as tools are needed to secure the nut and cotter pin.
Less Convenient for Temporary Use: Not ideal for applications requiring frequent removal and installation.
Comparison Summary
| Feature | Screw Pin Shackle | Bolt-Type Shackle |
|---|---|---|
| Pin Configuration | Threaded pin that screws into the body | Pin with a nut and cotter pin |
| Ease of Use | Quick and easy to install and remove | More time-consuming to install and remove |
| Applications | Temporary, field use, frequent removal | Permanent, long-term, critical load |
| Security | Risk of unscrewing under vibration | Very secure, nut and cotter pin prevent loosening |
| Installation | Requires no tools for installation | Requires tools for securing the nut and cotter pin |
| Typical Use Cases | General rigging, temporary connections | Long-term rigging, critical and heavy-duty applications |
Choosing the Right Shackle
- Screw Pin Shackle:
Best for situations where you need to frequently attach and detach the shackle.
Suitable for temporary setups and general-purpose rigging.
- Bolt-Type Shackle:
Ideal for permanent or long-term installations where maximum security is required.
Suitable for critical applications where accidental loosening of the pin cannot be tolerated.
Understanding the differences between these two types of shackles helps in selecting the right one for your specific application, ensuring safety, efficiency, and reliability in your lifting and rigging operations.
Chapt 8
How should shackles be stored and maintained?
Storing and Maintaining Shackles
Proper storage and maintenance of shackles are essential to ensure their longevity and safe operation. Here are the best practices for storing and maintaining shackles:
Storage of Shackles
Clean and Dry Environment:
Store shackles in a clean, dry location to prevent corrosion and rust. Avoid areas prone to moisture or chemical exposure.
Organized Storage:
Use bins, racks, or hooks to keep shackles organized by size and type. This prevents damage and makes it easier to find the correct shackle when needed.
Avoid Direct Sunlight and Extreme Temperatures:
Store shackles away from direct sunlight and extreme temperature variations, as these conditions can degrade materials over time.
Protect from Mechanical Damage:
Avoid storing shackles in a manner where they can be knocked over or where heavy objects might fall on them. Use padded or separated storage to prevent contact with other metal objects.
Labeling:
Clearly label storage areas with the size, type, and WLL of shackles. This helps in quick identification and ensures the correct shackle is used for each application.
Maintenance of Shackles
Regular Inspection:
Inspect shackles regularly for signs of wear, corrosion, cracks, or deformation. Pay special attention to the pin and threads.
Check the markings for WLL and ensure they are legible.
Cleaning:
Clean shackles with mild soap and water to remove dirt and grime. For more stubborn residues, use a wire brush or a non-abrasive scrubber.
Avoid using harsh chemicals that can damage the metal or coating.
Lubrication:
Apply a light coating of lubricant to the pin threads to ensure smooth operation and prevent seizing. Use a suitable lubricant for the environment, especially if the shackles are used in marine or corrosive environments.
Corrosion Prevention:
For shackles used in corrosive environments, consider using rust inhibitors or corrosion-resistant coatings.
Stainless steel shackles should be used in marine environments to prevent rust.
Proper Use and Handling:
Use shackles within their specified WLL and avoid shock loading or side loading.
Ensure the pin is properly seated and secured during use.
Storage After Use:
After use, especially in harsh environments, clean the shackles before storing them. Remove any contaminants such as salt, sand, or chemicals.
Periodic Testing:
For shackles used in critical applications, conduct periodic load testing to ensure they maintain their rated capacity. This should be done according to industry standards and regulations.
Summary of Storage and Maintenance Best Practices
Storage:
Store in a clean, dry, and organized environment.
Protect from direct sunlight, extreme temperatures, and mechanical damage.
Label storage areas clearly for easy identification.
Maintenance:
Regularly inspect for wear, corrosion, and damage.
Clean using mild soap and water; avoid harsh chemicals.
Lubricate pin threads to prevent seizing.
Use rust inhibitors or corrosion-resistant coatings in harsh environments.
Ensure proper use and handling, following the manufacturer’s guidelines.
Clean and store shackles properly after use.
Conduct periodic load testing for critical applications.
By adhering to these storage and maintenance practices, you can extend the lifespan of your shackles, maintain their performance, and ensure safety in your lifting and rigging operations.
Get the catalogue
Leave a request and we will send you the catalogue with Aulone rigging hardware by e-mail
86-15573139663
86-15363044363


