Answer: A non-rotating wire rope is designed to minimize or eliminate the tendency to spin or rotate under load. It achieves this through its construction, where the layers of strands are arranged to counteract each other’s torsional forces. This type of wire rope is commonly used in cranes and hoisting equipment, enhancing safety and precision by preventing the rope from spinning during lifting operations.
This article will continue the discussion on non-rotating wire rope from the following aspects.
Outline
Rotation Resistant and Non-Rotating Wire Rope
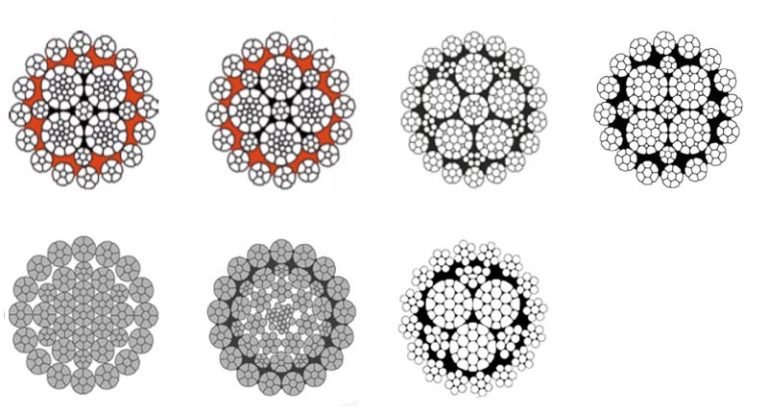
Rotation-resistant wire rope all called non-rotating Wire Rope
Rotation-resistant wire ropes, including both compacted and non-compacted types, are designed to minimize or eliminate rotation under load. Here are key examples and their structures:
Examples:
35WXK7 Wire Rope:
Structure: Compacted wire rope with 35 strands arranged in three layers.
First Layer: Inner strands laid in one direction.
Second Layer: Middle strands laid in the opposite direction.
Third Layer: Outer strands laid in the same direction as the first layer.
Core: Independent Wire Rope Core (IWRC).
Characteristics: Virtually eliminates rotation, high stability, and increased strength due to compacted strands.
Applications: High-precision lifting operations such as tower cranes and mobile cranes.
18×19 Wire Rope:
Structure: 18 strands, each containing 19 wires, designed to neutralize rotational forces.
Core: Fiber Core (FC) or IWRC.
Characteristics: Good balance of flexibility and non-rotating properties.
Applications: Various lifting and hoisting applications where non-rotating properties are critical.
34×7 Wire Rope:
Structure: 34 outer strands, each with 7 wires, over an IWRC.
Core: IWRC provides additional strength and stability.
Characteristics: Higher rotation resistance, greater breaking strength.
Applications: Multi-part hoist lines and critical lifting applications.
Detailed Comparison
| Feature | 35WXK7 Wire Rope | 18×19 Wire Rope | 34×7 Wire Rope |
| Core | IWRC | Fiber Core (FC) or IWRC | IWRC |
| Construction Layers | Three layers with alternating lay directions | Two layers with opposite lay directions | Two layers with opposite lay directions |
| Rotation Resistance | Virtually eliminates rotation under load | Virtually eliminates rotation under load | Minimizes rotation under load |
| Strength | High breaking strength, compacted | Moderate to high breaking strength | High breaking strength |
| Flexibility | Higher flexibility | Higher flexibility | Moderate flexibility |
| Typical Applications | High-precision lifting operations | Various lifting and hoisting applications | Multi-part hoist lines, critical lifting |
Selection Criteria
Application Requirements: Determine the degree of rotation resistance needed.
Load Capacity: Ensure the wire rope’s breaking strength matches the operational requirements.
Operational Environment: Consider factors like corrosion and abrasion.
Safety and Certification: Ensure the wire rope meets industry standards.
Conclusion
Choosing the right rotation-resistant (non-rotating) wire rope involves understanding the specific requirements of your lifting or hoisting application. The right selection ensures safe and efficient operations, minimizing the risk of rotation-related issues. Regular maintenance and inspection are crucial for the longevity and safety of these ropes.
35×7 (Compacted) Non-Rotating Wire Rope — 2160
Structure:
Compacted Design: The 35×7 wire rope consists of 35 strands arranged in three layers. The compacted design increases strength and reduces diameter.
First Layer: Inner strands laid in one direction.
Second Layer: Middle strands laid in the opposite direction.
Third Layer: Outer strands laid in the same direction as the first layer.
Core: Independent Wire Rope Core (IWRC) for added strength and stability.
Characteristics:
High Strength: 2160 grade indicates a high tensile strength of 2160 N/mm², making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Non-Rotating: Virtually eliminates rotation under load, ensuring stability during lifting operations.
Compacted Strands: Compaction increases the rope’s breaking strength and reduces its diameter, providing better performance and durability.
Durability: High resistance to wear and fatigue due to the compacted structure.
Applications:
High-Precision Lifting Operations: Ideal for tower cranes, mobile cranes, and other critical lifting equipment where rotation can be detrimental.
Construction and Industrial Use: Suitable for applications that require high strength and minimal rotation, ensuring safe and efficient operations.
Detailed Comparison
|
Feature |
35×7 (Compacted) Non-Rotating Wire Rope – 2160 Grade |
|
Core |
IWRC |
|
Construction Layers |
Three layers with alternating lay directions |
|
Rotation Resistance |
Virtually eliminates rotation under load |
|
Strength |
High breaking strength, 2160 mpa |
|
Flexibility |
Higher flexibility due to compacted strands |
|
Typical Applications |
High-precision lifting operations, construction, industrial use |
Selection Criteria
Application Requirements: Determine the degree of rotation resistance needed for high-precision lifting operations.
Load Capacity: Ensure the wire rope’s breaking strength matches the operational requirements.
Operational Environment: Consider factors such as corrosion and abrasion resistance needed for the specific environment.
Safety and Certification: Ensure the wire rope meets industry standards and certifications for safety.
Conclusion
The 35×7 (compacted) non-rotating wire rope in 2160 grade is an excellent choice for high-precision lifting and heavy-duty applications. Its high tensile strength, non-rotating properties, and compacted design ensure safe and efficient operations. Proper selection, maintenance, and regular inspection are crucial for the longevity and safety of this wire rope in demanding environments.
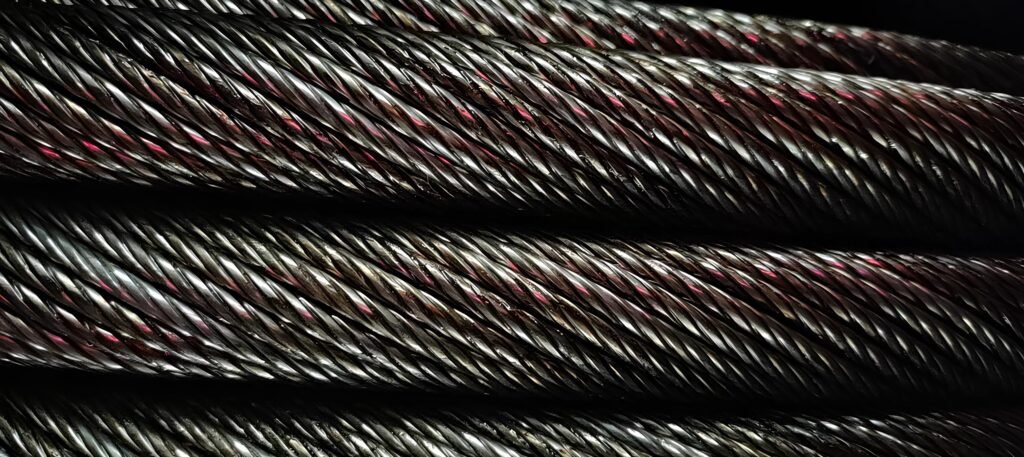
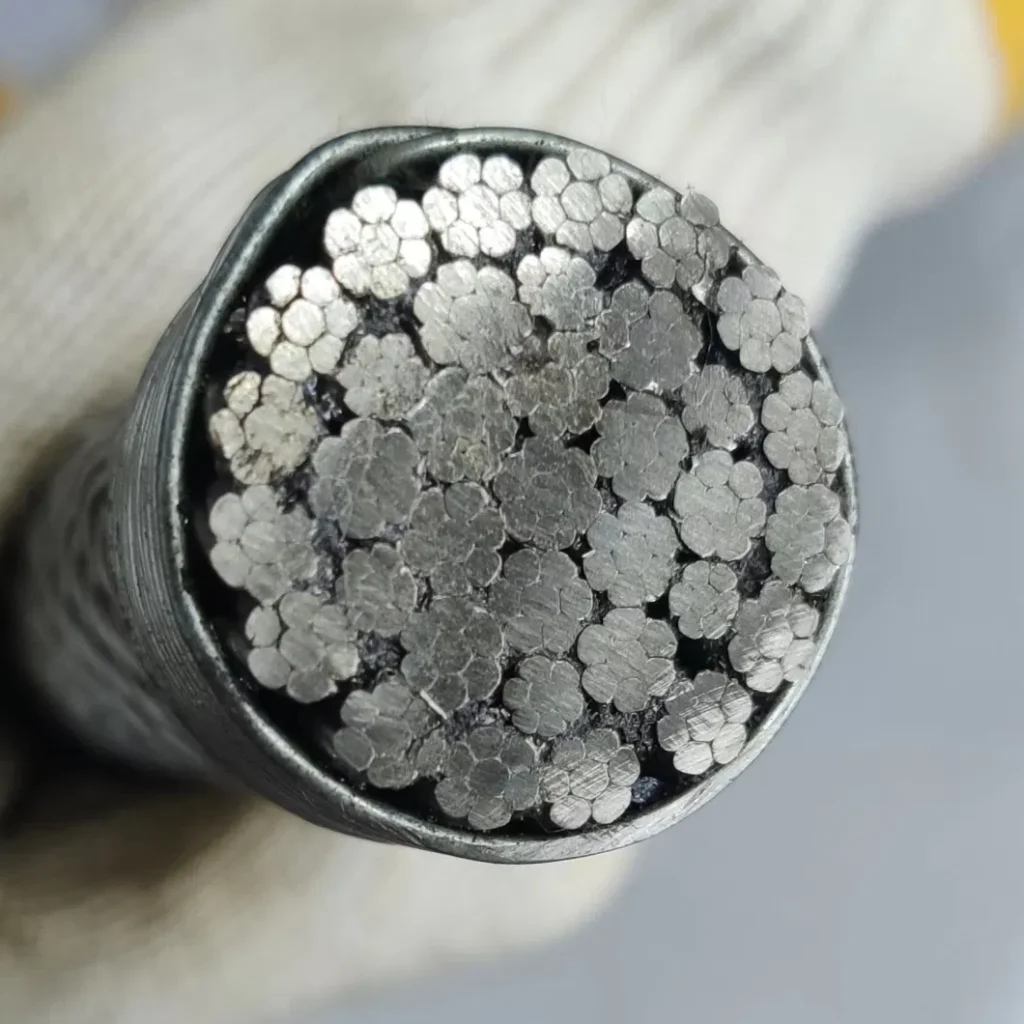

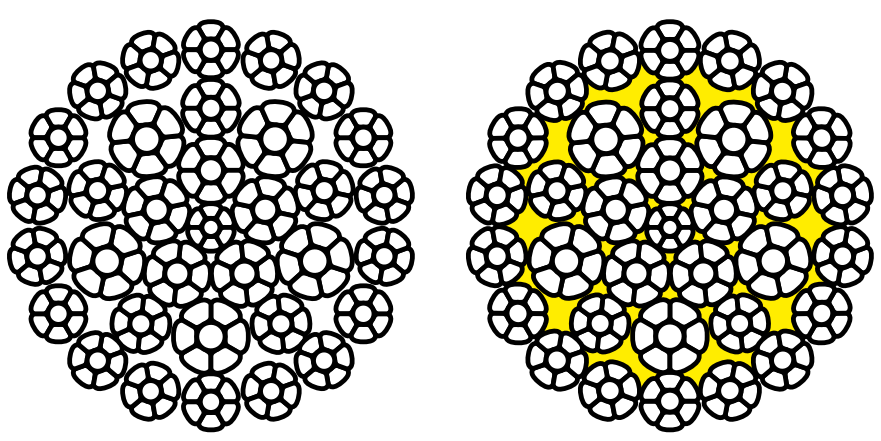

3/4″ 19×7 Rotation-Resistant Wire Rope
Structure:
Design: The 19×7 wire rope consists of 19 strands, each made up of 7 wires.
Core: Typically has a fiber core (FC) or an independent wire rope core (IWRC).
Strand Arrangement: Inner strands laid in one direction, outer strands laid in the opposite direction to balance the torque and minimize rotation.
Characteristics:
Diameter: 3/4 inch.
Rotation Resistance: Minimizes rotation under load, making it suitable for lifting operations where rotation needs to be controlled.
Flexibility: Offers good flexibility due to its construction, allowing it to handle bending stresses well.
Strength: Provides a balance between strength and flexibility, suitable for various lifting applications.
Applications:
Cranes: Ideal for overhead cranes, tower cranes, and mobile cranes where rotation resistance is necessary.
Hoisting Equipment: Suitable for use in hoisting equipment where controlled lifting is essential.
General Lifting Applications: Can be used in various industrial settings requiring rotation-resistant properties.
Detailed Characteristics
| Feature | 3/4″ 19×7 FC Wire Rope | 3/4″ 19×7 IWRC Wire Rope |
| Core | Fiber Core (FC) | Independent Wire Rope Core (IWRC) |
| Construction Layers | Two layers with opposite lay directions | Two layers with opposite lay directions |
| Rotation Resistance | Minimizes rotation under load | Minimizes rotation under load |
| Strength | Moderate breaking strength | Higher breaking strength |
| Flexibility | Higher flexibility | Moderate flexibility |
| Typical Applications | Cranes, hoisting equipment, general lifting | Cranes, hoisting equipment, general lifting |
Technical Specifications
Nominal Diameter: 3/4 inch (19.05 mm)
Construction: 19×7 (19 strands, each with 7 wires)
Core Types: FC or IWRC
Approximate Weight: Dependent on core type and specific construction, typically around 0.65 lbs/ft for FC and 0.70 lbs/ft for IWRC.
Selection Criteria
Application Requirements: Assess the specific lifting needs and the degree of rotation resistance required.
Load Capacity: Ensure the wire rope’s breaking strength meets the operational demands.
Core Type: Choose between FC and IWRC based on the desired balance of flexibility and strength.
Safety and Certification: Verify that the wire rope complies with relevant industry standards and certifications for safety.
Conclusion
The 3/4″ 19×7 rotation-resistant wire rope is well-suited for lifting and hoisting applications that require controlled rotation. Its balanced design offers good flexibility and strength, making it a reliable choice for cranes and other industrial equipment. Proper maintenance and regular inspection are essential to ensure safe and efficient operation.
Rotation-resistant and low-torque ropes
Rotation-resistant and low-torque ropes are essential for lifting and hoisting applications where minimizing rope spin and torsional forces is crucial. These ropes are designed to maintain stability under load, providing safer and more efficient operations.
Rotation-Resistant Ropes
Structure:
Design: Typically constructed with multiple layers of strands laid in opposing directions.
Core Types: Often feature either a Fiber Core (FC) or an Independent Wire Rope Core (IWRC) for added strength and stability.
Layer Configuration: Inner and outer strands are laid in opposite directions to counteract the torque generated under load.
Characteristics:
Minimized Rotation: The alternating lay directions balance the torsional forces, reducing rotation under load.
Good Flexibility: Multi-strand construction allows the rope to handle bending stresses effectively.
Strength and Stability: Designed to provide a balance between strength and flexibility, making them suitable for various lifting applications.
Examples:
19×7 Wire Rope:
Structure: 19 strands, each with 7 wires.
Core: Available with FC or IWRC.
Applications: Cranes, hoisting equipment, general lifting where moderate rotation resistance is needed.
34×7 Wire Rope:
Structure: 34 outer strands, each with 7 wires, typically over an IWRC.
Core: IWRC for additional strength and stability.
Applications: Multi-part hoist lines, critical lifting operations requiring higher rotation resistance.
Low-Torque Ropes
Structure:
Design: Constructed to minimize the build-up of internal torsional forces, ensuring minimal rope twist under load.
Core Types: Often features an IWRC for enhanced strength and torque resistance.
Layer Configuration: Multiple layers with opposing lay directions and sometimes compacted strands to further reduce torque.
Characteristics:
Minimal Torque Build-Up: Designed to prevent the accumulation of torsional forces, ensuring stable lifting operations.
High Strength: Typically made with high-strength materials and compacted strands for increased load capacity.
Durability: Enhanced wear resistance and longevity due to compacted design and high-quality materials.
Examples:
35×7 (Compacted) Wire Rope:
Structure: 35 strands arranged in three layers with compacted strands.
Core: IWRC for maximum strength and minimal elongation.
Applications: High-precision lifting operations such as tower cranes, mobile cranes, and other critical lifting equipment where both rotation resistance and low torque are essential.
18×19 Wire Rope:
Structure: 18 strands, each with 19 wires, designed to neutralize rotational forces.
Core: Typically has an IWRC or FC.
Applications: General lifting and hoisting applications requiring both flexibility and low torque.
Detailed Comparison
| Feature | 19×7 Wire Rope | 34×7 Wire Rope | 35×7 (Compacted) Wire Rope | 18×19 Wire Rope |
| Core | FC or IWRC | IWRC | IWRC | IWRC or FC |
| Construction Layers | Two layers with opposite lay directions | Two layers with opposite lay directions | Three layers with alternating lay directions | Two layers with opposite lay directions |
| Rotation Resistance | Minimizes rotation under load | Higher rotation resistance | Virtually eliminates rotation and torque | Virtually eliminates rotation |
| Strength | Moderate to high breaking strength | High breaking strength | High breaking strength, compacted | Moderate to high breaking strength |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility | Moderate flexibility | Higher flexibility | High flexibility |
| Typical Applications | Cranes, hoisting equipment, general lifting | Multi-part hoist lines, critical lifting | High-precision lifting operations | General lifting and hoisting applications |
Selection Criteria
Application Requirements: Identify the specific needs for rotation resistance and torque minimization.
Load Capacity: Ensure the wire rope’s breaking strength and load capacity meet operational requirements.
Core Type: Choose between FC and IWRC based on the desired balance of flexibility and strength.
Environmental Factors: Consider corrosion resistance, abrasion, and operational conditions affecting rope performance.
Safety Standards: Verify compliance with industry standards and certifications for safety and reliability.
Conclusion
Rotation-resistant and low-torque ropes are critical for ensuring safe and efficient lifting operations in various industrial applications. By understanding the structural differences and specific characteristics of ropes like 19×7, 34×7, 35×7 (compacted), and 18×19, users can select the most suitable rope for their needs. Regular maintenance and inspection are essential to maximize the lifespan and performance of these ropes in demanding environments.
Crane Ropes
Crane ropes are a critical component in the operation of cranes, used for lifting and moving heavy loads. Here’s a detailed overview of crane ropes, focusing on types, materials, and key considerations:
Types of Crane Ropes
Wire Ropes: The most common type used in crane operations. They are made up of multiple steel wires that form strands, which are then twisted around a core. The configuration of these ropes can vary based on the intended load and environmental conditions.
Synthetic Ropes: Made from high-strength, lightweight synthetic fibers like nylon, polyester, or aramids. These are used in applications where weight is a concern or where wire ropes might not be suitable due to environmental factors.
Common Wire Rope Configurations
6X19
Advantages:
1. Versatility: This configuration can adapt to various mechanical and environmental demands, making it suitable for a broad spectrum of lifting duties.
2. Durability: Robust against external abrasion, making it ideal for applications where the rope may come into contact with rough surfaces.
3. Flexibility: Its construction allows for sufficient bending without significant metal fatigue, critical for operations involving multiple direction changes.
6X36WS-IWRC
Advantages:
1. High Flexibility: Better suited for bending around large pulleys and drums, reducing wear and extending the rope’s operational life.
2. Fatigue Resistance: Its construction minimizes the impact of repeated stress, making it reliable for continuous use.
3. Load Capacity: Its structure supports heavier loads, enhancing the crane’s ability to handle substantial weights.
8XK26WS-IWRC (8 strands, K26 wire configuration, Wire Strand Core)
Advantages:
1. Higher Breaking Strength: Engineered for maximum strength, it can handle very heavy lifts.
2. Excellent Crush Resistance: The internal core supports the outer layers, preventing deformation under high stress.
3. Durability in Harsh Conditions: Performs well in tough working environments, resisting the effects of both mechanical and environmental stress.
35WXK7 and 15XK7 (Compacted Strand Structure)
Advantages:
1. High Break Load Capacity: The compacted design increases the contact area with the load, allowing for greater load-bearing capacity.
2. Reduced Internal Abrasion: The tight, compact structure minimizes movement within the rope, thereby reducing internal wear.
3. Smooth Surface: Less friction with sheaves and drums, which not only enhances efficiency but also extends the lifespan of both the rope and the hardware.
6XK36WS-IWRC (6 strands, K36 wire, Wire Strand Core)
Advantages:
1. Superior Fatigue Resistance: Excellent for high-cycle applications where the rope must endure numerous load cycles without failure.
2. Strong and Durable: Withstands harsh environmental conditions, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
Key Considerations
Diameter and Length: Determined by the crane’s capacity and the pulley systems used.
Core Type: Fiber cores are lighter and more flexible, while independent wire rope cores (IWRC) offer greater strength and heat resistance.
Lay Direction: Right lay or left lay, referring to the direction in which the strands are twisted. This affects the rope’s stability and how it interacts with the crane’s mechanisms.
Environment: Exposure to chemicals, heat, or abrasive materials can dictate the choice of rope material and construction.
Each of these configurations is tailored to meet specific operational demands of crane systems, offering optimized performance based on the unique challenges of different lifting environments. When selecting a wire rope for a crane, it’s crucial to consider these factors to ensure the rope not only meets the required performance standards but also contributes to safe and efficient operations.
Hoist Ropes For Tower Cranes
Hoist ropes for tower cranes are critical components in the lifting mechanisms of these cranes, which are essential for many construction projects. These ropes must be exceptionally strong, durable, and reliable, given their role in lifting heavy materials to significant heights. Here’s a detailed look at the key features, preferred configurations, and maintenance considerations for hoist ropes used in tower cranes:
-
Key Features of Hoist Ropes
1. High Tensile Strength: Essential to withstand the heavy loads typically lifted by tower cranes.
2. Flexibility: Important for winding and unwinding smoothly on the drum and sheaves without kinking or breaking.
3. Fatigue Resistance: Crucial for enduring the repeated stress of lifting cycles over the crane’s operational life.
4. Abrasion Resistance: Necessary to withstand wear from contact with other components like drums, sheaves, and guides.
For tower cranes, the hoist ropes like the 19X7, 35WXK7, and 35WXK7 with a plastic inset are specifically engineered to meet high standards of performance and durability in construction environments. Adding options like galvanization and lubrication further enhances their functionality. Here’s a comprehensive breakdown incorporating these additional requirements:
19X7 Advantages:
Non-Rotating: Essential for applications where the load might rotate during lifting, providing stability and safety.
Flexibility: Maintains flexibility necessary for efficient spooling on drum systems despite its non-rotating nature.
Durability: Exhibits high resistance to fatigue and abrasion, crucial for continuous heavy-duty use.
Usage: This configuration is typically utilized for main hoist lines on tower cranes, ideal in settings requiring precise load handling and control.
35WXK7 Advantages:
High Load Capacity: Compacted strands increase contact area with the load, offering enhanced load-bearing abilities.
Reduced Wear: The smooth exterior reduces external wear on sheaves and drums, while the compact design limits internal abrasion.
Stability: Provides excellent dimensional stability under load, which is vital for consistent operation.
Usage: Well-suited for hoisting where strength and durability are needed, such as in lifting heavy materials like concrete and steel.
35WXK7 with Plastic Inset Advantages:
Enhanced Wear Resistance: The plastic inset reduces internal friction, significantly extending the rope’s service life.
Improved Crush Resistance: Helps maintain the rope’s structure under high load, preventing deformation.
Better Lubrication Retention: The plastic aids in retaining lubrication, crucial for smooth operation and corrosion protection.
-
Usage: This rope is especially valuable in demanding construction environments requiring durability and high cycle loads.
Additional Enhancements
-
Galvanized Steel:
Corrosion Resistance: Galvanization adds a protective layer against rust and corrosion, which is especially important in outdoor or harsh environmental conditions.
Increased Durability: The zinc coating helps protect the steel from abrasive elements, prolonging the rope’s lifespan.
-
Lubrication:
Reduced Friction: Proper lubrication minimizes the friction between the wires and strands, reducing wear and heat build-up during operation.
Corrosion Protection: Lubricants can also help seal out moisture, preventing rust and corrosion.
Enhanced Flexibility: Keeps the rope flexible at the joints and bending points, essential for consistent performance over pulleys and drums.
Maintenance and Safety
- Regular Inspections: Critical for detecting early signs of wear, kinking, or corrosion. Both visual and tactile inspections are recommended.
- Proper Handling: Care must be taken to avoid sharp bends and overloading, which can stress the ropes and lead to premature failure.
- Routine Replacement: Establish a replacement schedule based on the rope’s condition and usage to ensure continuous safety and performance.
For clients requiring specific enhancements like galvanization and lubrication, these options not only fulfill the basic operational needs but also add significant value by extending the operational life and maintaining the performance integrity of hoist ropes in tower crane applications. These measures are crucial for ensuring safety, reliability, and efficiency in the rigorous demands of construction lifting operations.
Ask For A Quick Quote
Fill out a quick form to get a personalized quote tailored to your specific needs.