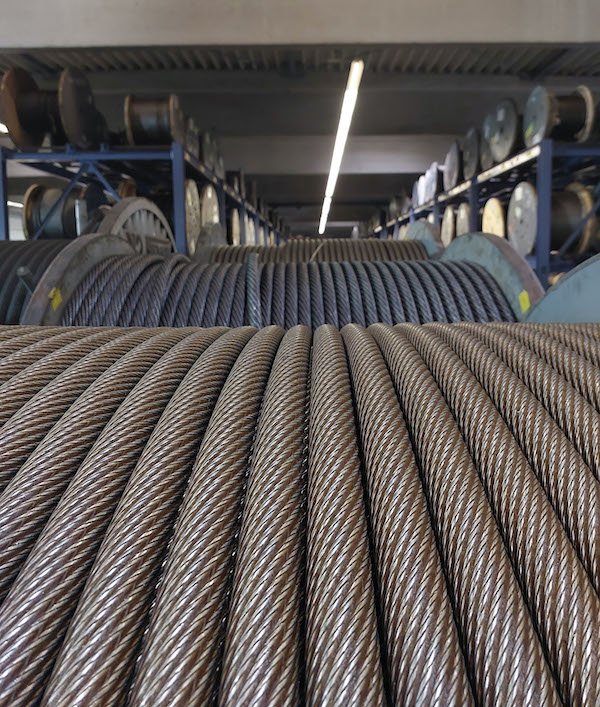
The strongest type of wire rope depends on the application, such as lifting, towing, suspension, or drilling. The key factors that determine wire rope strength include tensile strength (breaking force), rotation resistance, fatigue life, and wear resistance. Below is a detailed breakdown of the highest-strength wire rope types:
1. Ultra-High Strength Rotation-Resistant Wire Rope (Hoist Rope)
① 35WXK7 (35×7) Non-Rotating Wire Rope
- Structure: Composed of 35 wires in 7 strands, with an alternating lay structure where the inner and outer strands twist in opposite directions. This design significantly reduces rope rotation under load.
- Advantages:
- High breaking force (up to 2160 N/mm² or higher).
- Ideal for long-lifting applications such as tower cranes, offshore cranes, and ship cranes.
- Excellent rotation resistance, preventing load twisting that could cause instability.
- Disadvantages:
- Shorter bending fatigue life compared to other ropes (not ideal for frequent winding applications).
- Requires precise lubrication and handling to prevent premature wear.
2. High Breaking Force Compacted Strand Wire Rope
① 6XK36WS-IWRC (6-Strand Warrington Seale with IWRC)
- Structure: Six outer strands with a Warrington-Seale configuration and an independent wire rope core (IWRC). The strands are compacted, increasing the metallic cross-section.
- Advantages:
- Increased breaking force due to the larger metallic area.
- Superior wear resistance—ideal for applications with high loads and drum winding, such as crawler cranes and luffing ropes.
- Higher fatigue resistance compared to standard non-rotation-resistant ropes.
- Disadvantages:
- Heavier than standard wire ropes.
- Less flexible than rotation-resistant wire ropes.
② 8XK26WS-IWRC (8-Strand Warrington Seale with IWRC)
- Structure: Similar to 6XK36WS but with 8 outer strands, improving flexibility.
- Advantages:
- Even higher breaking force than 6-strand ropes due to increased strand count.
- Better flexibility and fatigue resistance, making it ideal for ship crane hoist ropes and luffing ropes.
- Disadvantages:
- Higher cost compared to standard wire ropes.
3. Fully Locked Coil Wire Rope (Static Load Applications)
- Structure: Features Z-shaped outer wires, providing a completely smooth surface.
- Advantages:
- Extremely high tensile strength, often exceeding 2000 MPa.
- Exceptional corrosion resistance, often galvanized or stainless steel-coated.
- Ideal for bridges, cable-stayed structures, and high-load suspension applications.
- Disadvantages:
- Very stiff—not suitable for dynamic bending applications.
- Requires specialized end fittings and installation techniques.
4. Plastic-Coated Core Wire Rope (EPIWRC) for Enhanced Durability
- Example: 8XK26WS-EPIWRC
- Structure: A compacted 8-strand rope with a plastic-coated steel core for added protection.
- Advantages:
- Superior wear resistance and increased fatigue life.
- Reduced internal friction, extending service life in demanding applications.
- Commonly used in offshore cranes, ship cranes, and piling rig wire ropes.
- Disadvantages:
- Slightly more expensive than standard wire ropes.
Which One is the Strongest?
- If you need maximum tensile strength for high-load lifting: 35WXK7 (Non-Rotating) or 8XK26WS-IWRC.
- If wear resistance and fatigue life are priorities: 6XK36WS-IWRC or 8XK26WS-IWRC.
- For structural and suspension applications: Fully Locked Coil Wire Rope is the best.
- Would you like a recommendation based on your specific application?