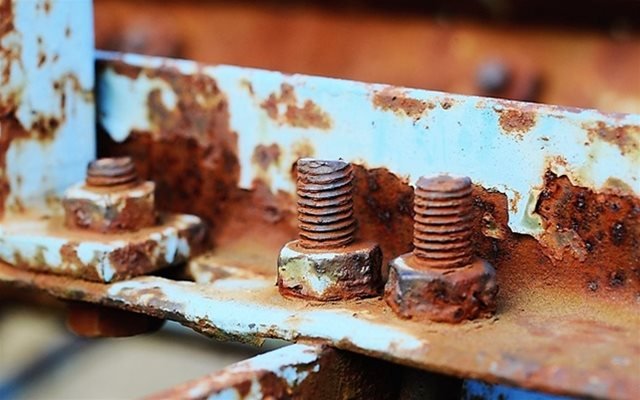
You’ve seen them endure for years. Then, you see rust on galvanized bolts. What happened? This problem often frustrates many.
Galvanized bolts can rust due to coating damage, improper application, environmental factors, or a bad galvanizing process. The zinc layer protects steel, but it is not permanent.
When I visited a client in Singapore, they showed me a bridge project. They used galvanized bolts. But some bolts showed rust spots. I told them we need to check the process. They were surprised.
What makes galvanized coatings fail over time?
You put time and money into galvanized bolts. You expect them to last. But sometimes, they fail. Why does this happen?
Galvanized coatings can fail over time because of harsh environments, physical damage, chemical exposure, or thinning of the zinc layer due to natural wear.

Dive Deeper: Understanding Galvanized Coating Failure
The zinc layer protects the steel. It acts as a barrier. It also provides cathodic protection. This means the zinc corrodes first. It saves the steel. But this protection is not endless.
Key Factors for Coating Failure:
- Environmental Causes:
- High Humidity: Constant moisture breaks down zinc faster.
- Saltwater Exposure: My products are used in marine environments. Salt is very corrosive. It speeds up zinc corrosion.
- Acid Rain: Pollutants in rain can be acidic. Acids dissolve zinc.
- Physical Damage:
- Scratches: If a bolt gets scratched, the zinc layer breaks. Steel gets exposed. Rust starts at that point.
- Impacts: Dropping a bolt or hitting it can chip the coating.
- Poor Handling: During shipping or installation, rough handling can hurt the coating. We make sure our specialized assemblies are handled with care.
- Chemical Exposure:
- Certain Chemicals: Some industrial chemicals react badly with zinc. This can quicken corrosion.
- Contact with Different Metals: Two different metals can create a galvanic reaction. This speeds up corrosion of one metal. For example, direct contact with copper can be bad for zinc.
- Galvanizing Process Issues:
- Poor Surface Preparation: The steel must be perfectly clean. If not, zinc will not bond well. This leads to early failure.
- Incorrect Zinc Thickness: The zinc layer must be thick enough. If it is too thin, it will not last long. My factory has four production lines. We control zinc thickness.
- Impure Zinc Bathes: The zinc itself must be pure. Impurities can weaken the coating.
The table below shows common reasons for coating failure.
| Type of Failure | Description | Preventive Measure |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental | Exposure to salt, acids, or high humidity | Use thicker coatings, apply sealants, or avoid harsh use |
| Physical | Scratches, chips, or impacts during handling | Careful handling, proper installation tools, protective caps |
| Chemical | Contact with strong acids, alkalis, or dissimilar metals | Isolate with non-conductive materials, choose correct environment |
| Process-related | Poor cleaning or incorrect zinc thickness | Ensure proper galvanizing standards, quality control |
How do environmental factors affect galvanized bolts?
Environmental conditions play a big role. They can make galvanized bolts rust fast. What are these factors? And how do they cause rust?
Environmental factors like high humidity, saltwater, acid rain, and extreme temperatures can accelerate the corrosion of galvanized bolts. These conditions degrade the protecting zinc layer.
Dive Deeper: Environmental Impacts on Galvanized Bolts
I work with clients in many countries. My wire ropes go to Singapore, Saudi Arabia, Russia, and Canada. Each place has different weather. The weather affects how long products last.
Specific Environmental Factors:
- Humidity and Moisture: Water is key for rust. Humid air has a lot of water. This means the zinc layer is always wet. Wet zinc corrodes faster. In very humid places, you might see rust sooner.
- Saltwater and Coastal Areas: My products are used near the sea. Marine wire rope needs good protection. Salt is very aggressive. It breaks down zinc layers quickly. Bolts used on docks or ships need extra care. This is why we offer specialized solutions.
- Acid Rain and Air Pollution: Cities and industrial areas have more air pollution. This pollution makes rain acidic. Acid eats zinc. My customers need high quality and good solutions. So, choosing the right galvanized bolt is vital.
- Temperature Extremes: Very hot or very cold weather can also impact galvanized coatings. Big temperature swings can cause the zinc layer to expand and contract. This can make small cracks. These cracks expose the steel.
- Soil Conditions: If bolts are underground, soil pH and moisture content matter. Acidic soils can corrode zinc faster.
We always check the environment where our products will be used. This helps us recommend the best product. We offer plastic impregnated and galvanized options.
What can you do to prevent galvanized bolts from rusting?
No one wants to see rust. You buy galvanized bolts for protection. So, how can you make sure they last? What steps can you take?
To prevent galvanized bolts from rusting, ensure proper installation, avoid physical damage, use compatible materials, and consider additional protective coatings or regular maintenance checks.
Dive Deeper: Steps to Prevent Rust
My client, Andri, from Australia, often talks about strict quality control. He needs certs like BV & CE. This is because he knows prevention is better than cure. Preventing rust saves money in the long run.
Effective Prevention Strategies:
- Proper Installation:
- Avoid Over-tightening: Too much torque can damage the zinc coating at the bolt head or threads. Use the right tools.
- Use Proper Tools: Tools that slip can scratch the coating.
- Handle with Care: Do not drop or drag bolts. Damage opens the door for rust.
- Additional Coatings:
- Paint or Sealants: Applying paint or a sealant over the galvanized layer gives extra protection. This is like putting a raincoat on a raincoat.
- Wax Coatings: Special waxes can provide a barrier against moisture and chemicals.
- Regular Inspections and Maintenance:
- Check for Damage: Look for scratches, chips, or dull spots.
- Touch-up Kits: Minor damage can often be repaired with zinc-rich paints. These paints are like a small galvanizing job. My team often advises on this.
- Cleaning: Remove dirt, salt, or chemicals regularly. Simple washing can extend life.
- Material Compatibility:
- Avoid Dissimilar Metals: Do not put galvanized bolts in direct contact with more noble metals, like copper. Use plastic washers or insulators.
- Proper Fasteners: If you use galvanized bolts, use galvanized nuts and washers too.
- Choose the Right Type of Galvanizing:
- Hot-Dip Galvanizing: This gives a thicker and more durable coating. My factory’s process ensures high quality. The EN12385-4 standard is important. It ensures breaking load and tensile strength.
My factory works hard to make high quality wire rope products. We focus on high tensile strength and high breaking load. This helps prevent early failures.
| Prevention Method | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Careful Handling | Prevent scratches and chips during transport/install | Protects integrity of zinc layer |
| Supplementary Coatings | Apply paint, sealant or wax over galvanized surface | Adds an extra barrier against elements |
| Regular Inspection | Check for damage or wear | Allows for early repair, prevents widespread rust |
| Material Isolation | Use insulators between dissimilar metals | Prevents accelerated galvanic corrosion |
| Quality Galvanizing | Ensure proper thickness, purity, and processing | Provides a strong and long-lasting initial protection |
Conclusion
Galvanized bolts can rust due to coating damage, harsh environments, or process flaws. Proper care and smart choices extend their life.