Are you frustrated with the frequent need to replace your tower crane ropes, impacting both your budget and project timelines?
At Aulone, we understand the importance of reliable equipment. Frequent replacements not only strain your budget but also lead to equipment downtime and lost business opportunities. Your investment in tower crane ropes should yield long-term, dependable performance, ensuring the safety and success of your operations.
What if there was a solution to prolong the life of your tower crane ropes? By implementing regular inspections and maintenance programs, you can maximize the lifespan of your ropes and minimize disruptions to your projects. Trust Aulone to provide you with top-quality, durable ropes that help you stay ahead of the competition.
In this article, you’ll find answers to the following questions:
- What inspections are necessary for your tower crane ropes?
- How should the ropes on your tower crane be replaced?
- What maintenance procedures do your crane ropes require?
What is ASME B30.3-2019 Tower Cranes?

Overview
ASME B30.3-2019 is a standard developed by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). The full name of ASME is the American Society of Mechanical Engineers. This standard provides comprehensive guidelines and requirements for the design, construction, installation, operation, inspection, testing, and maintenance of tower cranes to ensure their safe and efficient use.
Key Components of the Standard
-
Scope:
The standard applies to various configurations of tower cranes, including free-standing, climbing, and mobile base configurations. -
Definitions:
It provides clear definitions of terms used in the context of tower cranes to ensure consistent understanding and application of the standard. -
Design and Manufacturing:
Requirements for the design and manufacturing of tower cranes to ensure they have adequate strength and stability. -
Construction and Installation:
Guidelines for the proper construction and installation of tower cranes, ensuring they are erected and dismantled safely and according to manufacturer specifications. -
Operation:
Operational requirements, including the responsibilities of crane operators, riggers, and other personnel involved in lifting operations to ensure safety during crane operations. -
Inspection and Testing:
Detailed procedures for the inspection and testing of tower cranes to ensure they are in safe working condition. This includes pre-erection inspections, periodic inspections, and load testing. -
Maintenance:
Maintenance requirements to keep tower cranes in safe operating condition, including routine maintenance schedules and procedures for addressing any defects or issues. -
Safety Measures:
Safety measures and practices to protect workers and the public during crane operations, including load handling, signaling, and emergency procedures. -
Documentation:
Requirements for maintaining records related to the crane’s installation, inspections, tests, maintenance, and operation to ensure traceability and accountability.
Importance
Adherence to ASME B30.3-2019 helps ensure that tower cranes are used safely and effectively, minimizing the risk of accidents and enhancing overall operational efficiency. This standard is crucial for construction sites, ports, and other environments where tower cranes are utilized.
Following these guidelines is essential for maintaining safety and compliance with industry regulations.
What Inspections Shall Tower Crane Ropes Receive?
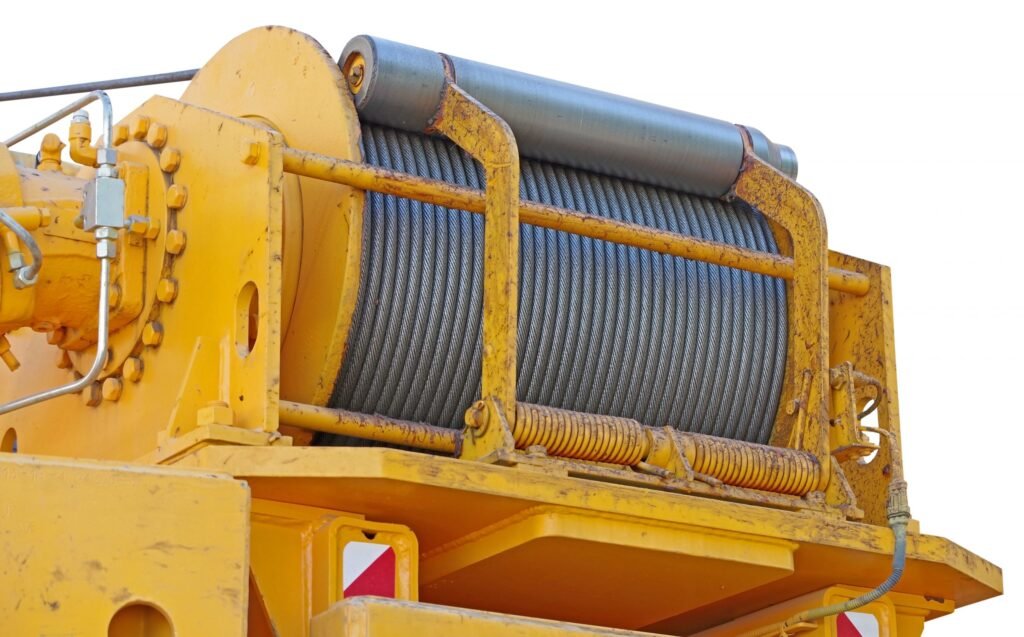

Tower crane ropes are critical components that require regular inspections to ensure safety and proper operation. The ASME B30.3-2019 standard outlines specific inspection requirements for tower crane ropes. Here are the key inspection types and their frequency:
Initial Inspection
Before First Use:
- New Ropes: A thorough inspection must be conducted before the crane is placed into service for the first time. This ensures that the ropes meet the manufacturer’s specifications and are free from defects.
Frequent Inspections
Daily to Monthly:
- Visual Inspections: These should be conducted by the crane operator or other designated personnel.
- Frequency: Inspections should occur at the beginning of each shift or at intervals determined by the crane’s usage and operating conditions.
- Check for:
Visible damage (e.g., cuts, abrasions, broken strands)
Proper reeving
Kinks or twists
Corrosion
Wear at contact points and end connections
Periodic Inspections
Monthly to Annual:
- Detailed Inspections: These should be more thorough and conducted by a qualified individual who has the training and experience to identify potential issues.
- Frequency: Typically conducted at intervals not exceeding one year, though more frequent inspections may be necessary based on the crane’s operating environment and usage.
- Check for:
Internal and external wear
Corrosion and lubrication condition
Broken wires
Diameter reduction due to wear
Proper spooling on the drum
End connections (e.g., sockets, swaged fittings)
Specific Inspection Details
- Wear and Abrasion: Inspect for uniform wear along the rope, especially at points where the rope runs over sheaves or contacts other surfaces.
- Broken Wires: Follow specific criteria for allowable broken wires as specified by the rope manufacturer or industry standards.
- Corrosion: Look for signs of rust or corrosion, which can significantly weaken the rope.
- Deformation: Check for any kinks, twists, bird-caging, or other deformities that may affect the rope’s integrity.
- Rope Diameter: Measure the rope diameter to ensure it is within acceptable limits, accounting for any reduction due to wear.
- End Connections: Ensure end connections are secure and free from damage. Properly seated and functioning end fittings are critical for safe operations.
Maintenance
- Lubrication:Ensure that the rope is properly lubricated as per the manufacturer’s recommendations to prevent corrosion and wear.
Record Keeping
- Documentation:Maintain detailed records of all inspections, noting the condition of the ropes, any defects found, and actions taken. This helps in tracking the rope’s history and planning replacements.
Regular and thorough inspections of tower crane ropes are essential to ensure the safety of lifting operations and to prevent accidents. Proper adherence to these guidelines helps in identifying potential issues early, ensuring timely maintenance or replacement of ropes, and maintaining overall operational safety and efficiency.
When Do Your Tower Crane Ropes Need to Be Replaced?
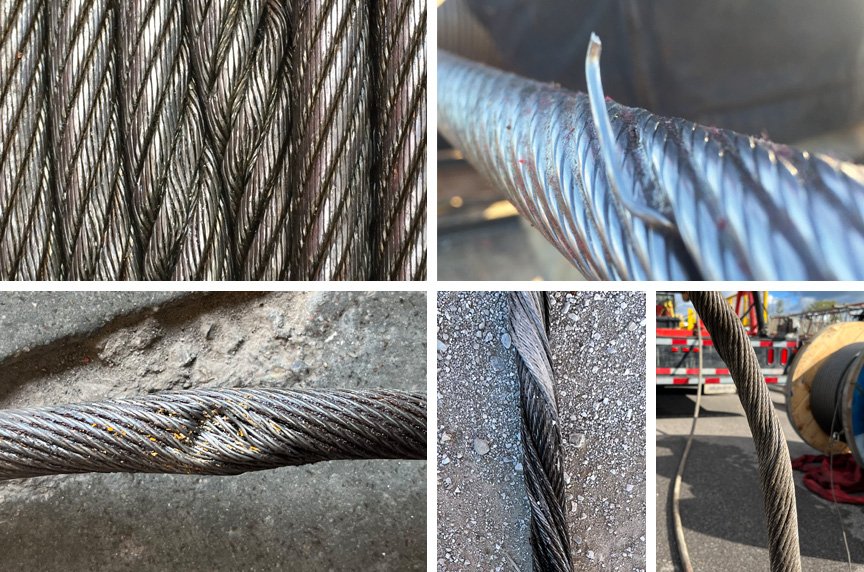

Replacing tower crane ropes at the appropriate time is essential for safety and operational efficiency. Here are the key indicators and criteria for rope replacement based on ASME B30.3-2019 and general industry best practices:
Key Indicators for Rope Replacement
-
Broken Wires:
Running Ropes: Replace if there are six or more randomly distributed broken wires in one lay length, or three or more broken wires in one strand in one lay length.
Standing Ropes: Replace if there are three or more broken wires in one lay length.
-
Wear and Abrasion:
Replace if there is a reduction of more than one-third of the original diameter of the outer wires.
Significant wear, flattening, or peening of the outer wires, especially at points of contact with sheaves and drums.
-
Corrosion:
Replace if there is significant corrosion that affects the strength of the rope.
Pitting corrosion on the surface or internal corrosion that compromises the rope’s integrity.
-
Deformation:
Replace if there are kinks, twists, bird-caging, crushing, or other deformations that distort the rope’s structure.
Any distortion that affects the ability of the rope to pass through sheaves or lay properly on drums.
-
Reduction in Diameter:
Replace if the rope’s diameter is reduced by more than 10% due to wear.
Regularly measure and monitor the rope diameter to detect any significant reduction.
-
Heat Damage:
Replace if the rope shows signs of heat damage such as discoloration, annealing, or welding splatter, which can alter the material properties of the rope.
-
Rope End Conditions:
Replace if end connections show signs of wear, cracking, or other damage.
Regularly inspect the integrity of swaged fittings, sockets, and terminations.
Additional Considerations
-
Manufacturer’s Recommendations:
Always follow the rope manufacturer’s specific replacement criteria and guidelines.
-
Usage and Environment:
Consider the operating environment (e.g., exposure to chemicals, saltwater, extreme temperatures) and the intensity of usage when determining replacement intervals.
High-cycle applications or harsh environments may necessitate more frequent replacements. -
Inspection Findings:
Base replacement decisions on the results of regular inspections (both frequent and periodic).
If any inspection reveals conditions that do not meet safety standards, replace the rope immediately. -
Documentation:
Maintain detailed records of all inspections, maintenance activities, and rope replacements.
Document any incidents or unusual wear patterns to aid in future maintenance planning and safety assessme.
Summary
To ensure the safe and efficient operation of tower cranes, it is crucial to replace ropes when they show signs of significant wear, damage, or degradation as outlined above. Regular inspections, adherence to replacement criteria, and detailed record-keeping are key to preventing accidents and maintaining the longevity of the equipment.
How Can You Maintain Your Tower Crane Ropes?
Regular Inspections
- Frequent Inspections:
- Daily Visual Checks: Perform visual inspections at the beginning of each shift to look for visible signs of wear, damage, or misalignment.
- Operational Monitoring: Continuously monitor the rope during operations for any unusual noises, vibrations, or movements that might indicate a problem.
- Periodic Inspections:
- Monthly/Quarterly Checks: Conduct more detailed inspections at least monthly, or more frequently if the crane is heavily used or operates in harsh conditions.
- Use Tools: Employ tools like calipers to measure rope diameter, magnifying glasses to inspect wire breaks, and magnetic flux leakage (MFL) devices to detect internal corrosion.
- Comprehensive Annual Inspections:
- Full-Length Inspection: Once a year, inspect the entire length of the rope, including sections that are not visible during normal operations.
- Third-Party Inspections: Consider hiring a qualified third-party inspector to conduct a thorough and unbiased inspection.
Lubrication
- Proper Lubrication:
- Lubricant Type: Use the manufacturer-recommended lubricant suitable for the rope type and operating conditions.
- Application: Apply lubricant evenly along the entire length of the rope, ensuring it penetrates to the core. Re-lubricate as per the manufacturer’s guidelines or more frequently in harsh environments.
- Avoid Over-Lubrication:
- Excessive lubrication can attract dirt and debris, which can increase wear. Apply the right amount to ensure optimal protection without attracting contaminants.
Cleaning
- Regular Cleaning:
- Remove Debris: Periodically clean the rope to remove dirt, dust, and other contaminants that can cause abrasion and wear.
- Cleaning Agents: Use mild cleaning agents that do not degrade the rope material or its lubricant.
- Post-Cleaning Inspection:
- After cleaning, conduct a thorough inspection to identify any hidden damage or wear that may have been obscured by dirt.
Proper Handling and Storage
- Handling:
- Avoid Kinks and Twists: Handle the rope carefully to avoid kinks, twists, or crushing. Use proper lifting techniques and equipment to move the rope.
- Correct Reeling: Ensure the rope is reeled onto drums correctly to avoid crushing and ensure even distribution of load.
- Storage:
- Environment: Store ropes in a clean, dry, and well-ventilated area, away from direct sunlight, chemicals, and extreme temperatures.
- Support: Store coils and reels on supports that prevent deformation and ensure they are not in contact with the ground or other surfaces that can cause damage.
Training and Safety Practices
- Operator Training:
- Ensure that all crane operators and maintenance personnel are trained in proper rope handling, inspection, and maintenance techniques.
- Safety Protocols:
- Implement safety protocols for working with ropes, including the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and following safety guidelines during inspections and maintenance activities.
Documentation and Record Keeping
- Inspection Records:
- Maintain detailed records of all inspections, including the date, inspector’s name, findings, and any maintenance actions taken.
- Maintenance Logs:
- Keep logs of all maintenance activities, including lubrication schedules, cleaning procedures, and any repairs or replacements performed.
- Rope History:
- Document the complete history of each rope, including its installation date, usage, incidents, and any changes in operating conditions.
Proactive Replacement
- Timely Replacement:
- Replace ropes before they reach the end of their safe operational life. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and industry standards for rope replacement intervals.
- Monitoring Usage:
- Track the usage of each rope, including load cycles, environmental conditions, and any incidents of overloading or abnormal wear. Use this information to predict when a rope will need replacement.
Manufacturer’s Guidelines
- Adherence to Specifications:
- Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance guidelines and specifications for the rope. This includes using recommended lubricants, following proper inspection intervals, and adhering to load limits.
- Consultation for Specialized Conditions:
- If the crane operates in unique or harsh conditions, consult the manufacturer for specialized maintenance advice tailored to those conditions.

Crane Ropes
Top-notch crane ropes, ready for your project – get a quote from Aulone!