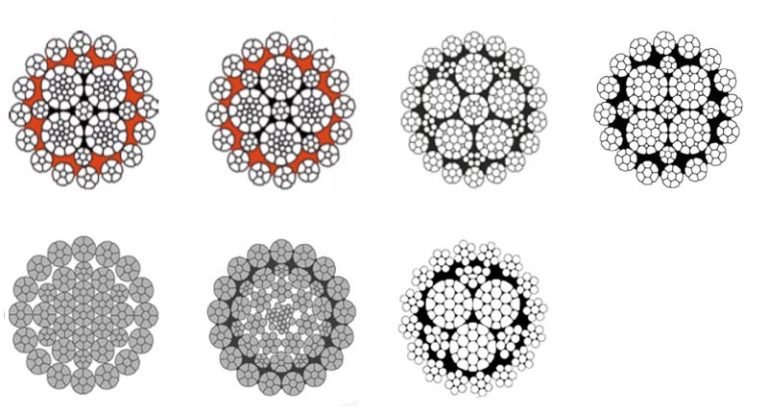
Do you struggle to choose the right wire rope? I know the confusion and delays it can cause in projects.
Wire ropes vary by type, construction, and weight. Understanding these factors ensures safety, efficiency, and correct selection for lifting or marine applications.
I remember a client once miscalculated rope weight, causing shipment delays. Let me guide you through everything I’ve learned about wire ropes and their weights.
What are the main types of wire ropes?
Wire ropes come in many types. Each suits different lifting or pulling tasks.
The main types are standard steel ropes, galvanized, stainless steel, and plastic-impregnated. Each type offers specific strength, corrosion resistance, and flexibility.
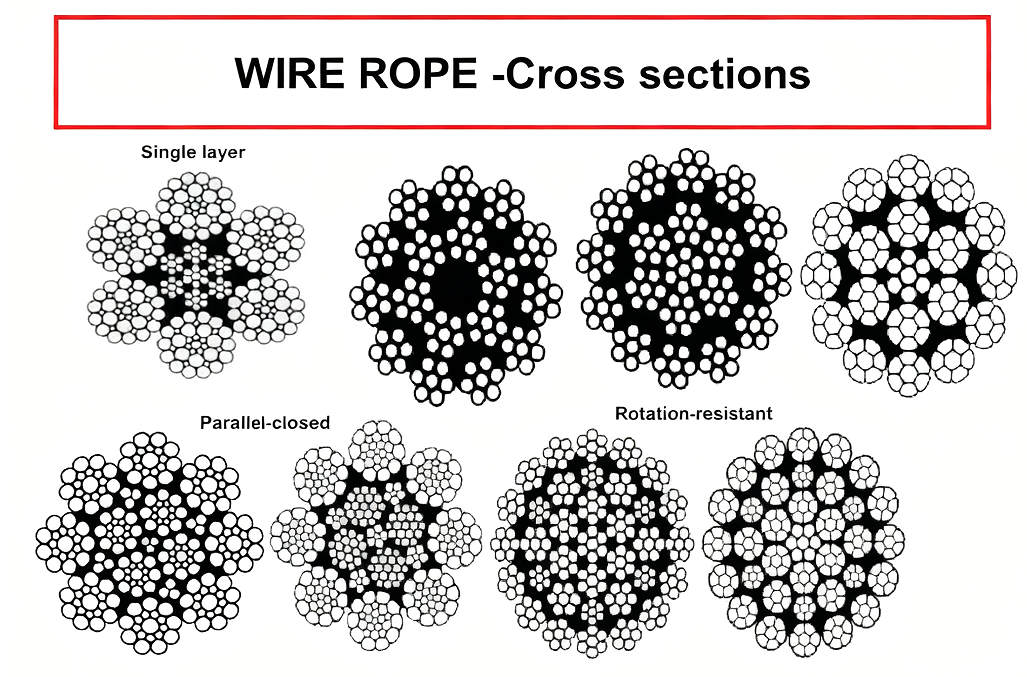
Wire ropes are defined by their strand arrangement and core type. The construction affects flexibility, strength, and durability. Here’s a breakdown:
| Construction | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| 6×19 IWRC | 6 strands, 19 wires each, Independent Wire Rope Core | General lifting, cranes |
| 6×36 WS | 6 strands, 36 wires, Warrington Seale | Flexibility, bending over sheaves |
| 35WXK7 | Compacted, low rotation | High-lift cranes, mining |
| 8xK26 | 8 strands, 26 wires | Marine, anti-rotation |
| 6xK36 WS-IWRC | Galvanized or stainless | Construction and heavy lifting |
| 8xK26 WS-EPIWRC | Plastic coated | Offshore, marine applications |
Each construction has unique characteristics. For example, compacted ropes like 35WXK7 resist rotation in cranes. Flexible ropes like 6×36 WS handle multiple bending cycles. Choosing the wrong construction can reduce rope life by 30% or more.
How to calculate wire rope weight?
Weight matters for lifting limits and shipping. Knowing exact rope weight saves money and prevents overload.
Rope weight depends on diameter, material, and construction. Standard tables or formulas help calculate kilograms per meter or feet.
Step-by-step weight calculation:
- Identify rope diameter and construction.
- Use manufacturer’s weight tables or formulas.
- Multiply length by weight per unit length.
For example, a 20mm 35WXK7 rope weighs about 2 kg per meter. If your project needs 100 meters, total weight is 200 kg.
| Diameter (mm) | Type | Weight (kg/m) |
|---|---|---|
| 12 | Galvanized 6×19 | 0.6 |
| 16 | Stainless 6×36 | 1.07 |
| 20 | Compacted 35WXK7 | 2 |
| 24 | 19XK7 | 2.65 |
| 32 | Galvanized 8xK26 | 5.12 |
I always double-check weight before dispatch. A small miscalculation can cause shipment delays or lifting accidents.
Why does wire rope certification matter?
Certifications confirm rope quality. They protect you from accidents or product failure.
Certified ropes meet EN12385-4, DNV, BV, or ABS standards. This guarantees tensile strength, load capacity, and proper testing.

Wire ropes undergo tensile tests, break load verification, and non-destructive testing. Certified ropes:
- Ensure lifting safety
- Reduce downtime
- Provide insurance compliance
| Certificate | Meaning | When Needed |
|---|---|---|
| EN12385-4 | European lifting standard | Construction, cranes |
| DNV | Marine certification | Offshore, shipping |
| BV | Bureau Veritas | Heavy industrial projects |
| ABS | American Bureau of Shipping | Marine, ship lifting |
For instance, I once supplied a crane project using non-certified rope. The client faced insurance issues after an inspection. After switching to DNV-certified rope, the problem was solved immediately. Certification is not just paper—it saves real money and time.
How to choose the right rope for your project?
Different tasks need different ropes. Choosing wrong leads to accidents and extra costs.
Consider load, bending cycles, environment, and flexibility. Select type, construction, and coating accordingly.

Matching rope to project prevents failure. Here are examples:
| Application | Recommended Rope | Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Crane lifts | 35WXK7 | Low rotation, high load |
| Ship rigging | 6×36 WS | Corrosion resistant |
| Mining | 6×19 IWRC | High tensile strength |
| Elevators | 8xK26 | Smooth bending, flexible |
I often ask clients about environment and lifting cycles before suggesting a rope. For offshore work, galvanization or plastic coating is essential. In indoor elevators, flexibility is more important than tensile strength. Small adjustments like these extend rope life and save maintenance costs.
What affects wire rope lifespan?
Many factors shorten rope life. Understanding them helps avoid surprises and extra cost.
Wear, corrosion, overloading, bending, and lack of lubrication reduce rope lifespan. Proper handling and inspection prevent early failures.

- Lubrication: Keeps wires from rusting
- Proper storage: Avoid kinks and sharp bends
- Inspection: Check for broken wires, core damage
- Avoid overloading: Never exceed working load limit
- Environment: Corrosive environments need galvanized or stainless steel ropes
| Factor | Impact | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Rust & corrosion | Weakens rope | Galvanized or stainless |
| Overload | Causes sudden failure | Use correct WLL |
| Frequent bending | Wire fatigue | Flexible construction |
| Poor storage | Kinks, deformation | Store on reels properly |
I share this advice with every client. It prevents downtime and ensures operations remain smooth.
How do coating and impregnation help?
Coatings protect ropes. They increase rope life and reduce maintenance.
Galvanized, stainless steel, and plastic-impregnated ropes resist corrosion and abrasion. This improves safety and reduces long-term costs.

- Galvanized: Best for outdoor, humid, or marine use
- Stainless steel: Corrosion-resistant, good for chemicals and offshore
- Plastic-impregnated: Protects wires, reduces friction, extends bending life
| Rope Type | Feature | Ideal Use |
|---|---|---|
| Galvanized 6×36 WS | Rust-resistant | Construction, offshore |
| Stainless 6×19 IWRC | Chemical-resistant | Marine, mining |
| Plastic-impregnated 8xK26 | Reduced friction | Offshore, bending-heavy projects |
I often recommend plastic impregnation for marine cranes. It reduces wire fatigue and improves safety for repeated lifting cycles.
Conclusion
Choosing the right wire rope ensures safety, efficiency, and project success. Weight, construction, type, coating, and certification all matter.